Page 250 - Modular design for machine tools
P. 250
210 Engineering Design for Machine Tool Joints
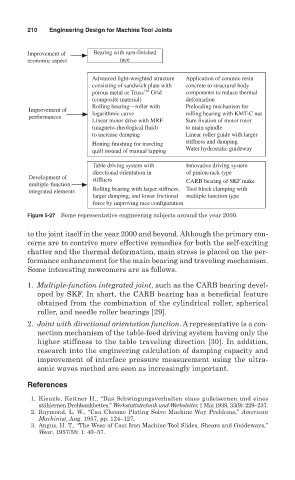
Improvement of Bearing with turn-finished
economic aspect race
Advanced light-weighted structure Application of ceramic resin
consisting of sandwich plate with concrete to structural body
TM
porous metal or Truss Grid components to reduce thermal
(composite material) deformation
Rolling bearing—roller with Preloading mechanism for
Improvement of
logarithmic curve rolling bearing with KMT-C nut
performances
Linear motor drive with MRF Sure fixation of motor rotor
(magneto-rheological fluid) to main spindle
to increase damping Linear roller guide with larger
Honing finishing for traveling stiffness and damping
Water hydrostatic guideway
quill instead of manual lapping
Table driving system with Innovative driving system
directional orientation in of pinion-rack type
Development of stiffness
multiple-function CARB bearing of SKF make
integrated elements Rolling bearing with larger stiffness, Tool block clamping with
larger damping, and lower frictional multiple function type
force by improving race configuration
Figure 5-27 Some representative engineering subjects around the year 2000.
to the joint itself in the year 2000 and beyond. Although the primary con-
cerns are to contrive more effective remedies for both the self-exciting
chatter and the thermal deformation, main stress is placed on the per-
formance enhancement for the main bearing and traveling mechanism.
Some interesting newcomers are as follows.
1. Multiple-function integrated joint, such as the CARB bearing devel-
oped by SKF. In short, the CARB bearing has a beneficial feature
obtained from the combination of the cylindrical roller, spherical
roller, and needle roller bearings [29].
2. Joint with directional orientation function. A representative is a con-
nection mechanism of the table-feed driving system having only the
higher stiffness to the table traveling direction [30]. In addition,
research into the engineering calculation of damping capacity and
improvement of interface pressure measurement using the ultra-
sonic waves method are seen as increasingly important.
References
1. Kienzle, Kettner H., “Das Schwingungsverhalten eines gußeisernen und eines
stählernen Drehbankbettes,” Werkstattstechnik und Werksleiter, 1 Mai 1939, 33(9): 229–237.
2. Raymond, L. W., “Can Chrome Plating Solve Machine Way Problems,” American
Machinist, Aug. 1957, pp. 124–127.
3. Angus, H. T., “The Wear of Cast Iron Machine Tool Slides, Shears and Guideways,”
Wear, 1957/58; 1: 40–57.