Page 16 - Multidimensional Chromatography
P. 16
Introduction 5
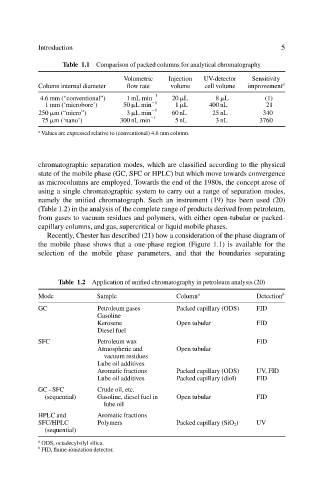
Table 1.1 Comparison of packed columns for analytical chromatography
Volumetric Injection UV-detector Sensitivity
Column internal diameter flow rate volume cell volume improvement a
4.6 mm (“conventional”) 1 mL min 1 20 L 8 L (1)
1 mm (‘microbore’) 50 L min 1 1 L 400 nL 21
250 m (“micro”) 3 L min 1 60nL 25 nL 340
75 m (‘nano’) 300 nL min 1 5nL 3 nL 3760
a
Values are expressed relative to (conventional) 4.6 mm column.
chromatographic separation modes, which are classified according to the physical
state of the mobile phase (GC, SFC or HPLC) but which move towards convergence
as microcolumns are employed. Towards the end of the 1980s, the concept arose of
using a single chromatographic system to carry out a range of separation modes,
namely the unified chromatograph. Such an instrument (19) has been used (20)
(Table 1.2) in the analysis of the complete range of products derived from petroleum,
from gases to vacuum residues and polymers, with either open-tubular or packed-
capillary columns, and gas, supercritical or liquid mobile phases.
Recently, Chester has described (21) how a consideration of the phase diagram of
the mobile phase shows that a one-phase region (Figure 1.1) is available for the
selection of the mobile phase parameters, and that the boundaries separating
Table 1.2 Application of unified chromatography in petroleum analysis (20)
Mode Sample Column a Detection b
GC Petroleum gases Packed capillary (ODS) FID
Gasoline
Kerosene Open tubular FID
Diesel fuel
SFC Petroleum wax FID
Atmospheric and Open tubular
vacuum residues
Lube oil additives
Aromatic fractions Packed capillary (ODS) UV, FID
Lube oil additives Packed capillary (diol) FID
GC–SFC Crude oil, etc.
(sequential) Gasoline, diesel fuel in Open tubular FID
lube oil
HPLC and Aromatic fractions
SFC/HPLC Polymers Packed capillary (SiO 2 ) UV
(sequential)
a
ODS, octadecylsilyl silica.
b
FID, flame-ionization detector.