Page 209 - Multidimensional Chromatography
P. 209
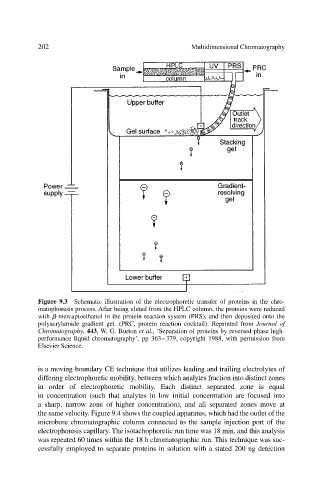
202 Multidimensional Chromatography
Figure 9.3 Schematic illustration of the electrophoretic transfer of proteins in the chro-
matophoresis process. After being eluted from the HPLC column, the proteins were reduced
with -mercaptoethanol in the protein reaction system (PRS), and then deposited onto the
polyacrylamide gradient gel. (PRC, protein reaction cocktail). Reprinted from Journal of
Chromatography, 443, W. G. Burton et al., ‘Separation of proteins by reversed-phase high-
performance liquid chromatography’, pp 363–379, copyright 1988, with permission from
Elsevier Science.
is a moving-boundary CE technique that utilizes leading and trailing electrolytes of
differing electrophoretic mobility, between which analytes fraction into distinct zones
in order of electrophoretic mobility. Each distinct separated zone is equal
in concentration (such that analytes in low initial concentration are focused into
a sharp, narrow zone of higher concentration), and all separated zones move at
the same velocity. Figure 9.4 shows the coupled apparatus, which had the outlet of the
microbore chromatographic column connected to the sample injection port of the
electrophoresis capillary. The isotachophoretic run time was 18 min, and this analysis
was repeated 60 times within the 18 h chromatographic run. This technique was suc-
cessfully employed to separate proteins in solution with a stated 200 ng detection