Page 216 - Multidimensional Chromatography
P. 216
Multidimensional Electrodriven Separations 209
capacity of 650 was obtained from this HPLC–CZE system. Rapid fingerprinting of
proteins was one of the suggested possible applications for this technique (25). The
success of this two-dimensional technique led to the possibility of coupling HPLC-
CZE to other techniques to further increase dimensionality and total peak capacity.
9.11 THREE-DIMENSIONAL SIZE EXCLUSION
CHROMATOGRAPHY–REVERSE PHASE LIQUID
CHROMATOGRAPHY–CAPILLARY ZONE ELECTROPHORESIS
Moore and Jorgenson combined the rapid two-dimensional separation achieved by
LC-CZE with SEC to make the first comprehensive three-dimensional separation
involving an electrodriven component in 1995. Size exclusion chromatography sepa-
rated the analytes over a period of several hours while the reverse phase HPLC–CZE
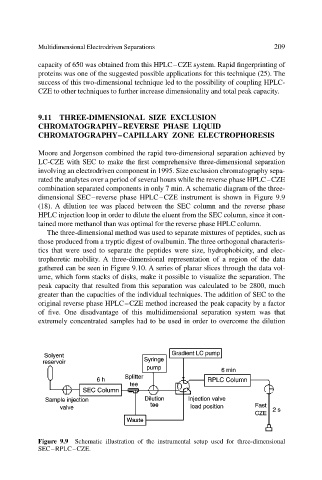
combination separated components in only 7 min. A schematic diagram of the three-
dimensional SEC–reverse phase HPLC–CZE instrument is shown in Figure 9.9
(18). A dilution tee was placed between the SEC column and the reverse phase
HPLC injection loop in order to dilute the eluent from the SEC column, since it con-
tained more methanol than was optimal for the reverse phase HPLC column.
The three-dimensional method was used to separate mixtures of peptides, such as
those produced from a tryptic digest of ovalbumin. The three orthogonal characteris-
tics that were used to separate the peptides were size, hydrophobicity, and elec-
trophoretic mobility. A three-dimensional representation of a region of the data
gathered can be seen in Figure 9.10. A series of planar slices through the data vol-
ume, which form stacks of disks, make it possible to visualize the separation. The
peak capacity that resulted from this separation was calculated to be 2800, much
greater than the capacities of the individual techniques. The addition of SEC to the
original reverse phase HPLC–CZE method increased the peak capacity by a factor
of five. One disadvantage of this multidimensional separation system was that
extremely concentrated samples had to be used in order to overcome the dilution
Figure 9.9 Schematic illustration of the instrumental setup used for three-dimensional
SEC–RPLC–CZE.