Page 228 - Multidimensional Chromatography
P. 228
222 Multidimensional Chromatography
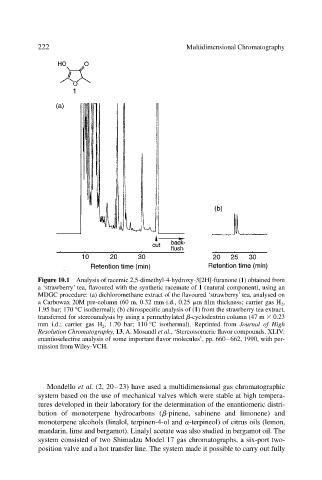
Figure 10.1 Analysis of racemic 2,5-dimethyl-4-hydroxy-3[2H]-furanone (1) obtained from
a ‘strawberry’ tea, flavoured with the synthetic racemate of 1 (natural component), using an
MDGC procedure: (a) dichloromethane extract of the flavoured ‘strawberry’ tea, analysed on
a Carbowax 20M pre-column (60 m, 0.32 mm i.d., 0.25 m film thickness; carrier gas H 2 ,
1.95 bar; 170 °C isothermal); (b) chirospecific analysis of (1) from the strawberry tea extract,
transferred for stereoanalysis by using a permethylated -cyclodextrin column (47 m 0.23
mm i.d.; carrier gas H 2 , 1.70 bar; 110 °C isothermal). Reprinted from Journal of High
Resolution Chromatography, 13, A. Mosandl et al., ‘Stereoisomeric flavor compounds. XLIV:
enantioselective analysis of some important flavor molecules’, pp. 660–662, 1990, with per-
mission from Wiley-VCH.
Mondello et al. (2, 20–23) have used a multidimensional gas chromatographic
system based on the use of mechanical valves which were stable at high tempera-
tures developed in their laboratory for the determination of the enantiomeric distri-
bution of monoterpene hydrocarbons ( -pinene, sabinene and limonene) and
monoterpene alcohols (linalol, terpinen-4-ol and -terpineol) of citrus oils (lemon,
mandarin, lime and bergamot). Linalyl acetate was also studied in bergamot oil. The
system consisted of two Shimadzu Model 17 gas chromatographs, a six-port two-
position valve and a hot transfer line. The system made it possible to carry out fully