Page 323 - Multidimensional Chromatography
P. 323
Industrial and Polymer Applications 313
Solutions of the styrene–acrylonitrile copolymer were separated on a micro-size
exclusion column (50 cm 250 m i.d., packed with Zorbax PSM-1000), using
THF as the mobile phase, and with UV detection at 220 nm, and specific fractions
were then transferred into an on-line pyrolysis chamber. Within this chamber, the
non-volatile polymer fractions were pyrolyzed and the products separated on a capil-
lary GC column (50 m 0.25 mm i.d., coated with 5% phenylmethylsilicone). The
variability in composition was studied by obtaining the area ratios of the styrene and
acrylonitrile peaks that were formed in each molecular size fraction. The relative
composition of this polymer in the six fractions over the molecular-weight range
4
4
from 1.1 10 to 1.8 10 was determined to be 5.96, with a relative standard
deviation of 2.4%. The relative composition of the styrene–acrylonitrile copolymer
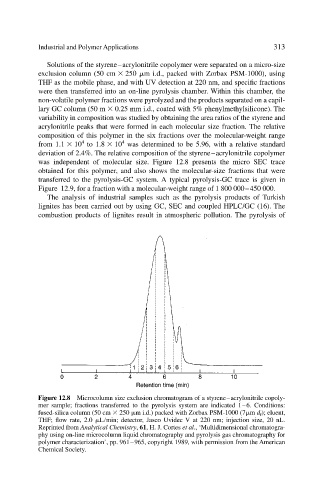
was independent of molecular size. Figure 12.8 presents the micro SEC trace
obtained for this polymer, and also shows the molecular-size fractions that were
transferred to the pyrolysis-GC system. A typical pyrolysis-GC trace is given in
Figure 12.9, for a fraction with a molecular-weight range of 1 800 000–450 000.
The analysis of industrial samples such as the pyrolysis products of Turkish
lignites has been carried out by using GC, SEC and coupled HPLC/GC (16). The
combustion products of lignites result in atmospheric pollution. The pyrolysis of
Figure 12.8 Microcolumn size exclusion chromatogram of a styrene–acrylonitrile copoly-
mer sample; fractions transferred to the pyrolysis system are indicated 1–6. Conditions:
fused-silica column (50 cm 250 m i.d.) packed with Zorbax PSM-1000 (7 m d f ); eluent,
THF; flow rate, 2.0 L min; detector, Jasco Uvidec V at 220 nm; injection size, 20 nL.
Reprinted from Analytical Chemistry, 61, H. J. Cortes et al., ‘Multidimensional chromatogra-
phy using on-line microcolumn liquid chromatography and pyrolysis gas chromatography for
polymer characterization’, pp. 961–965, copyright 1989, with permission from the American
Chemical Society.