Page 421 - Multidimensional Chromatography
P. 421
Forensic and Toxicological Applications 413
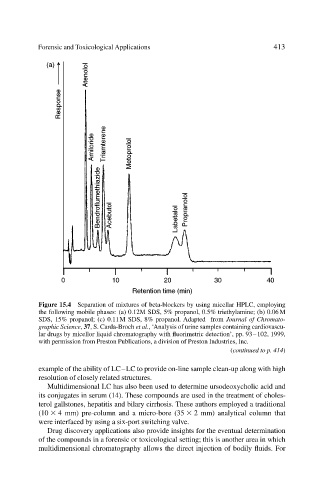
Figure 15.4 Separation of mixtures of beta-blockers by using micellar HPLC, employing
the following mobile phases: (a) 0.12M SDS, 5% propanol, 0.5% triethylamine; (b) 0.06M
SDS, 15% propanol; (c) 0.11M SDS, 8% propanol. Adapted from Journal of Chromato-
graphic Science, 37, S. Carda-Broch et al., ‘Analysis of urine samples containing cardiovascu-
lar drugs by micellor liquid chromatography with fluorimetric detection’, pp. 93–102, 1999,
with permission from Preston Publications, a division of Preston Industries, Inc.
(continued to p. 414)
example of the ability of LC–LC to provide on-line sample clean-up along with high
resolution of closely related structures.
Multidimensional LC has also been used to determine ursodeoxycholic acid and
its conjugates in serum (14). These compounds are used in the treatment of choles-
terol gallstones, hepatitis and bilary cirrhosis. These authors employed a traditional
(10 4 mm) pre-column and a micro-bore (35 2 mm) analytical column that
were interfaced by using a six-port switching valve.
Drug discovery applications also provide insights for the eventual determination
of the compounds in a forensic or toxicological setting; this is another area in which
multidimensional chromatography allows the direct injection of bodily fluids. For