Page 169 - Multifunctional Photocatalytic Materials for Energy
P. 169
Metal-based semiconductor nanomaterials for thin-film solar cells 155
8.2 Fabrication of metal-based semiconductor
nanomaterials
8.2.1 Titanium dioxide (TiO 2 )
Titanium (Ti) is the ninth most abundant element in the Earth’s crust. Titanium dioxide
(TiO 2 ), which is the most common compound of titanium, is a typical n-type semi-
conductor. TiO 2 has three crystalline forms: anatase, rutile, and brookite; their struc-
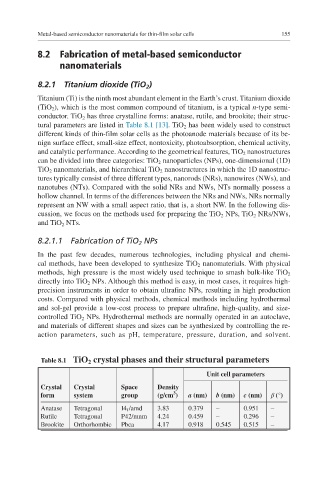
tural parameters are listed in Table 8.1 [13]. TiO 2 has been widely used to construct
different kinds of thin-film solar cells as the photoanode materials because of its be-
nign surface effect, small-size effect, nontoxicity, photoabsorption, chemical activity,
and catalytic performance. According to the geometrical features, TiO 2 nanostructures
can be divided into three categories: TiO 2 nanoparticles (NPs), one-dimensional (1D)
TiO 2 nanomaterials, and hierarchical TiO 2 nanostructures in which the 1D nanostruc-
tures typically consist of three different types, nanorods (NRs), nanowires (NWs), and
nanotubes (NTs). Compared with the solid NRs and NWs, NTs normally possess a
hollow channel. In terms of the differences between the NRs and NWs, NRs normally
represent an NW with a small aspect ratio, that is, a short NW. In the following dis-
cussion, we focus on the methods used for preparing the TiO 2 NPs, TiO 2 NRs/NWs,
and TiO 2 NTs.
8.2.1.1 Fabrication of TiO 2 NPs
In the past few decades, numerous technologies, including physical and chemi-
cal methods, have been developed to synthesize TiO 2 nanomaterials. With physical
methods, high pressure is the most widely used technique to smash bulk-like TiO 2
directly into TiO 2 NPs. Although this method is easy, in most cases, it requires high-
precision instruments in order to obtain ultrafine NPs, resulting in high production
costs. Compared with physical methods, chemical methods including hydrothermal
and sol-gel provide a low-cost process to prepare ultrafine, high-quality, and size-
controlled TiO 2 NPs. Hydrothermal methods are normally operated in an autoclave,
and materials of different shapes and sizes can be synthesized by controlling the re-
action parameters, such as pH, temperature, pressure, duration, and solvent.
Table 8.1 TiO 2 crystal phases and their structural parameters
Unit cell parameters
Crystal Crystal Space Density
3
form system group (g/cm ) a (nm) b (nm) c (nm) β (°)
Anatase Tetragonal I4 1 /amd 3.83 0.379 – 0.951 –
Rutile Tetragonal P42/mnm 4.24 0.459 – 0.296 –
Brookite Orthorhombic Pbca 4.17 0.918 0.545 0.515 –