Page 168 - Multifunctional Photocatalytic Materials for Energy
P. 168
154 Multifunctional Photocatalytic Materials for Energy
DSSC/QDSC PSCs
Ag cathode Ag cathode Ag cathode Ag cathode
Hole-transporter HTM Porous perovskite
(Spiro-OMeTAD) Dye HTM ETA HTM
TiO 2 AI 2 O 3
Thin film
perovskite
Compact TiO 2 Compact TiO 2 Compact TiO 2 Compact TiO 2
SnO 2 :F(FTO)Anode SnO 2 :F(FTO)Anode SnO 2 :F(FTO)Anode SnO 2 :F(FTO)Anode
Glass Glass Glass Glass
(A) (B)
OPV
Cathode Anode
Cathode Anode CIL AIL
CIL AIL Active layer Active layer
ICL ICL
Active layer Active layer
Active layer Active layer
AIL CIL AIL CIL
Transparent anode Transparent cathode Transparent anode Transparent cathode
Substrate Substrate Substrate Substrate
hν hν hν hν
(C)
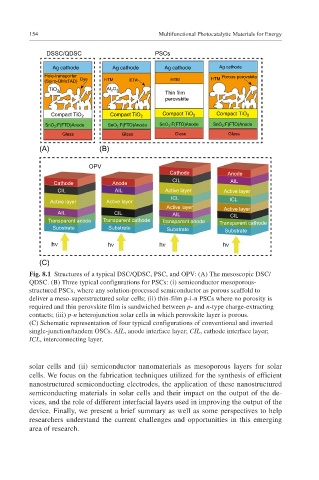
Fig. 8.1 Structures of a typical DSC/QDSC, PSC, and OPV: (A) The mesoscopic DSC/
QDSC. (B) Three typical configurations for PSCs: (i) semiconductor mesoporous-
structured PSCs, where any solution-processed semiconductor as porous scaffold to
deliver a meso-superstructured solar cells; (ii) thin-film p-i-n PSCs where no porosity is
required and thin perovskite film is sandwiched between p- and n-type charge-extracting
contacts; (iii) p-n heterojunction solar cells in which perovskite layer is porous.
(C) Schematic representation of four typical configurations of conventional and inverted
single-junction/tandem OSCs. AIL, anode interface layer; CIL, cathode interface layer;
ICL, interconnecting layer.
solar cells and (ii) semiconductor nanomaterials as mesoporous layers for solar
cells. We focus on the fabrication techniques utilized for the synthesis of efficient
nanostructured semiconducting electrodes, the application of these nanostructured
semiconducting materials in solar cells and their impact on the output of the de-
vices, and the role of different interfacial layers used in improving the output of the
device. Finally, we present a brief summary as well as some perspectives to help
researchers understand the current challenges and opportunities in this emerging
area of research.