Page 272 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 272
4.5 STRUCTURE CONTROL OF NANOPARTICLE COLLECTIVES BY SINTERING AND BONDING FUNDAMENTALS
Table 4.5.3
Classification of collide process.
Method Force Actors
Watchers Movers
Slip casting Capillarity Particles Liquid
Both ions
Pressure/vacuum casting Capillarity Particles Liquid
and/or pressure Both ions
and/or suction
Centrifugal force casting Centrifugal force Both ions Particles
Liquid
Tape casting Mechanical Liquid
Particles
Both ions
EPD Electrohydrodynamics Liquid Particles
Electrochemical Both ions
suspension. Therefore, to understand the characteris-
tic of each particle in the solvent is essential. A
ceramic particle is charged in the solvent especially in
an aqueous solution due to the interaction between the
particle surface (or surface adsorbed species) and sol-
vent. The magnitude of the surface potential is esti-
Suspension mated by measuring the zeta potential.
During practical processing, the systems where par-
ticle dispersion can be controlled by pH are very lim-
ited. In some systems, particles do not have a high
enough zeta potential or problems such as hydration or
dissolution happen. Therefore, the adsorption of a
polyelectrolyte with –COOH or –NH on the powder
3
surface is usually conducted. In this case, an electros-
Consolidated layer
teric stabilization is expected due to the surface charge
of the electrolyte and adsorption of the polymer [3].
According to the DLVO theory [4], the colloidal
stability is governed by the total interparticle poten-
Mold
tial energy (V ), which is the summation of the repul-
T
sive potential energy (V ), and van der Waals
R
interaction potential energy (V ).
A
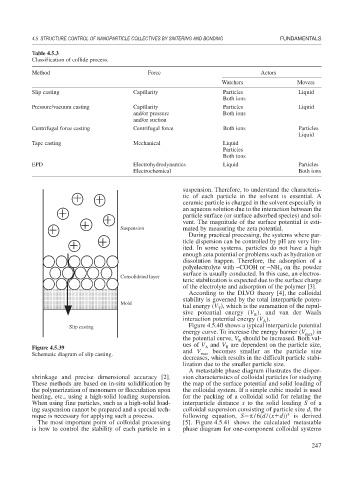
Figure 4.5.40 shows a typical interparticle potential
Slip casting
energy curve. To increase the energy barrier (V max ) in
the potential curve, V should be increased. Both val-
R
ues of V and V are dependent on the particle size,
R
Figure 4.5.39 and V A becomes smaller as the particle size
Schematic diagram of slip casting. max
decreases, which results in the difficult particle stabi-
lization due to the smaller particle size.
A metastable phase diagram illustrates the disper-
shrinkage and precise dimensional accuracy [2]. sion characteristics of colloidal particles for studying
These methods are based on in-situ solidification by the map of the surface potential and solid loading of
the polymerization of monomers or flocculation upon the colloidal system. If a simple cubic model is used
heating, etc., using a high-solid loading suspension. for the packing of a colloidal solid for relating the
When using fine particles, such as a high-solid load- interparticle distance x to the solid loading S of a
ing suspension cannot be prepared and a special tech- colloidal suspension consisting of particle size d, the
3
nique is necessary for applying such a process. following equation, S /6(d/(x d)) is derived
The most important point of colloidal processing [5]. Figure 4.5.41 shows the calculated metastable
is how to control the stability of each particle in a phase diagram for one-component colloidal systems
247