Page 274 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 274
4.5 STRUCTURE CONTROL OF NANOPARTICLE COLLECTIVES BY SINTERING AND BONDING FUNDAMENTALS
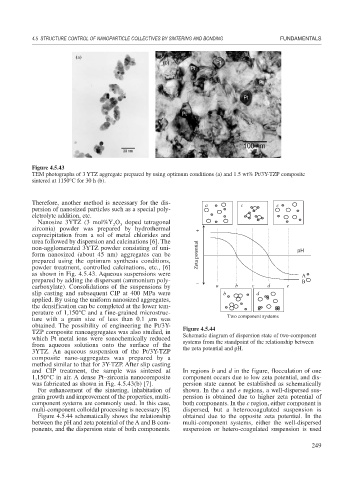
Figure 4.5.43
TEM photographs of 3 YTZ aggregate prepared by using optimum conditions (a) and 1.5 wt% Pt/3Y-TZP composite
sintered at 1150°C for 30 h (b).
Therefore, another method is necessary for the dis- a c e
persion of nanosized particles such as a special poly-
eletrolyte addition, etc.
Nanosize 3YTZ (3 mol%Y O doped tetragonal
3
2
zirconia) powder was prepared by hydrothermal +
coprecipitation from a sol of metal chlorides and
urea followed by dispersion and calcinations [6]. The
non-agglomerated 3YTZ powder consisting of uni- pH
form nanosized (about 45 nm) aggregates can be Zeta potential
prepared using the optimum synthesis conditions,
powder treatment, controlled calcinations, etc., [6]
as shown in Fig. 4.5.43. Aqueous suspensions were A
prepared by adding the dispersant (ammonium poly- – B
carboxylate). Consolidations of the suspensions by a b c d e
slip casting and subsequent CIP at 400 MPa were b d
applied. By using the uniform nanosized aggregates,
the densification can be completed at the lower tem-
perature of 1,150°C and a fine-grained microstruc- Two component systems
ture with a grain size of less than 0.1 m was
obtained. The possibility of engineering the Pt/3Y- Figure 4.5.44
TZP composite nanoaggregates was also studied, in Schematic diagram of dispersion state of two-component
which Pt metal ions were sonochemically reduced systems from the standpoint of the relationship between
from aqueous solutions onto the surface of the the zeta potential and pH.
3YTZ. An aqueous suspension of the Pt/3Y-TZP
composite nano-aggregates was prepared by a
method similar to that for 3Y-TZP. After slip casting
and CIP treatment, the sample was sintered at In regions b and d in the figure, flocculation of one
1,150°C in air. A dense Pt–zirconia nanocomposite component occurs due to low zeta potential, and dis-
was fabricated as shown in Fig. 4.5.43(b) [7]. persion state cannot be established as schematically
For enhancement of the sintering, inhabitation of shown. In the a and e regions, a well-dispersed sus-
grain growth and improvement of the properties, multi- pension is obtained due to higher zeta potential of
component systems are commonly used. In this case, both components. In the c region, either component is
multi-component colloidal processing is necessary [8]. dispersed, but a heterocoagulated suspension is
Figure 4.5.44 schematically shows the relationship obtained due to the opposite zeta potential. In the
between the pH and zeta potential of the A and B com- multi-component systems, either the well-dispersed
ponents, and the dispersion state of both components. suspension or hetero-coagulated suspension is used
249