Page 415 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 415
7.2 NANOPARTICLES AND ENVIRONMENT FUNDAMENTALS
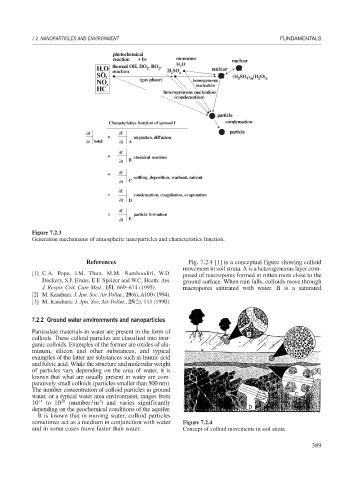
photochemical
reaction + hv monomer nuclear
H O
thermal OH, HO , RO ,
H O 2 2 2 nuclear
2 reaction H SO 4
2
SO 2 (H 2 SO 4 ) m (H 2 O) n
(gas phase) homogeneous
NO x nucleation
HC
heterogeneous nucleation
(condensation)
particle
Characteristics function of aerosol f condensation
∂f ∂f particle
= migration, diffusion
∂t total ∂t A
∂f
+ chemical reaction
∂t B
+ ∂f
settling, deposition, washout, rainout
∂t C
∂f
+ condensation, coagulation, evaporation
∂t D
∂f
+ particle formation
∂t E
Figure 7.2.3
Generation mechanisms of atmospheric nanoparticles and characteristics function.
References Fig. 7.2.4 [1] is a conceptual figure showing colloid
movement in soil strata. A is a heterogeneous layer com-
[1] C.A. Pope, J.M. Thun, M.M. Namboodiri, W.D. posed of macropores formed in rotten roots close to the
Dockery, S.J. Evans, E.F. Speizer and W.C. Heath: Am. ground surface. When rain falls, colloids move through
J. Respir. Crit. Care Med., 151, 669–674 (1995). macropores saturated with water. B is a saturated
[2] M. Kasahara: J. Jpn. Soc. Air Pollut., 29(6), A100 (1994).
[3] M. Kasahara: J. Jpn. Soc. Air Pollut., 25(2), 115 (1990).
7.2.2 Ground water environments and nanoparticles
Particulate materials in water are present in the form of
colloids. These colloid particles are classified into inor-
ganic colloids. Examples of the former are oxides of alu-
minum, silicon and other substances, and typical
examples of the latter are substances such as humic acid
and fulvic acid. While the structure and molecular weight
of particles vary depending on the area of water, it is
known that what are usually present in water are com-
paratively small colloids (particles smaller than 500 nm).
The number concentration of colloid particles in ground
water, or a typical water area environment, ranges from
3
10 11 to 10 20 (number/m ) and varies significantly
depending on the geochemical conditions of the aquifer.
It is known that in moving water, colloid particles
sometimes act as a medium in conjunction with water Figure 7.2.4
and in some cases move faster than water. Concept of colloid movements in soil strata.
389