Page 416 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 416
FUNDAMENTALS CH. 7 ENVIRONMENTAL AND SAFETY ISSUES WITH NANOPARTICLES
homogeneous porous layer such as a sand layer, and 7.2.3 Nanoparticles in exhaust gases
most of the colloid particles are trapped. The mecha-
nism of partical trap in this layer is explained by the In most cases, nanoparticles in exhaust gases are
sand filtration theory. C and D are a gravel layer and a studied from the viewpoint of the influence of total
rock bed, respectively, and both have high water perme- particulate matters on the environment. The term
ability with large gaps and cracks. Particles can also “nanoparticles” is used only in a few cases, “fine
pass through easily. particles” is usually used for investigation. Since
Safety and movement characteristics of colloid par- nanoparticles are part of fine particles, this section
ticles have a significant influence on the movement of will be described from this perspective.
materials such as ionized molecules in aquatic envi- Major sources of combustion exhaust gases are sta-
ronments. Since fine particles such as nanoparticles tionary large-scale combustors and diesel engines for
in particular are highly stable as colloid particles, it stationary and portable use.
will be very important in the future to understand For stationary combustors, fuels such as coal, oil,
their influence. At the same time, these characteristics and gas are used. Lighter fuels have a lower rate of
are considered to have a high potential to be devel- particulate emission, but have a higher fine particle
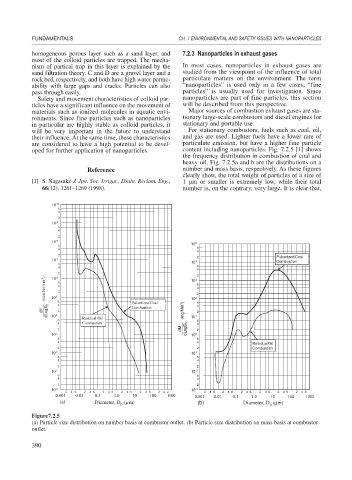
oped for further application of nanoparticles. content including nanoparticles. Fig. 7.2.5 [1] shows
the frequency distribution in combustion of coal and
heavy oil. Fig. 7.2.5a and b are the distributions on a
Reference number and mass basis, respectively. As these figures
clearly show, the total weight of particles of a size of
[1] S. Nagasaki: J. Jpn. Soc. Irrigat., Drain. Reclam. Eng., 1 m or smaller is extremely low, while their total
66(12), 1261–1269 (1998). number is, on the contrary, very large. It is clear that,
10 10 10
10
6 6 6
4 4 4
2 2 2
10 10 9 9
6 6 6
4 4 4
2 2 2
10 10 10 8 8 8
10
6 6 6 6 10 5 5
4 4 4 4 6 6 6
4 4 4
2 2 2 2
2 2 2 Pulverized Coal
10 10 10 7 7 7 10 4 4 Combustion
10
6 6 6 6
4 4 4 4 6 6 6
4 4 4
2 2 2 2
2 2 2
(number/cm 3 ) (number/cm 3 ) (number/cm 3 10 10 10 5 5 5 6 6 6 6 4 4 4 4 2 2 2 2 10 2 2 6 6 6 4 4 4 2 2 2
10 10 10
6 6 6
10
10 3
3
10
dLogD P dLogD P dLogD P 6 6 6 6 4 4 4 4 Pulverized Coal 6 6 6 4 4 4
Combustion
dN dN dN 4 4 4 2 2 2 2 (mg/Nm 3 ) (mg/Nm 3 ) (mg/Nm 3 ) 2 2 2
10 10 10
10
6 6 6 6 Residual Oil 10 1 1 6 6 6
4 4 4 4 Combustion 4 4 4
dM dM dM dLogD P dLogD P dLogD P
2 2 2 2 2 2 2
10 10 10 3 3 3 10 0 0
10
6 6 6 6 6 6 6
4 4 4 4 4 4 4 Residual Oil
t
2 2 2 2 2 2 2 Combustion
10
10
10 2 2 2 10 -1 -1
10
6 6 6 6 6 6 6
4 4 4 4 4 4 4
2 2 2 2 2 2 2
10
10 -2
10 1 1 1 10 -2
10
6 6 6 6 6 6 6
4 4 4 4 4 4 4
2 2 2 2 2 2 2
10 0 0 0 10 -3 -3
10
10
10
2 2 2 4 6 6 6 2 2 2 4 6 6 6 22 4 66 6 22 2 4 66 2 22 4 6 66 222 4 666 2 4 6 6 6 2 4 6 6 6 2 4 6 6 6 2 4 6 6 6 2 4 6 6 6 2 4 6 6 6
1.0
0.01
0.1
10
0.001
0.001 0.01 0.1 1.0 10 100 1 1000 0.0 0 1 0 0.01 0.1 1.0 10 0 1 100 1 1000
100
.01
1.0
.1
0
1
0.001
00
(a) Diameter, D (µm) (b) Diameter, D (μm)
p
p
Figure7.2.5
(a) Particle size distribution on number basis at combustor outlet. (b) Particle size distribution on mass basis at combustor
outlet.
390