Page 417 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 417
7.2 NANOPARTICLES AND ENVIRONMENT FUNDAMENTALS
while the total quantity of particulate material is far significant contribution of carbon particles formed
larger in coal combustion than in oil combustion, the in the gas phase.
difference is less when it comes to particles 1 m or Also in the case of ash from heavy oil combus-
less in diameter, including nanoparticles. tion, there are large particles of a carbon residue
Most of the particles contained in pulverized coal type generated from sprayed liquid particles and
combustion exhaust gases are considered to be particles formed in the gas phase as well. As in the
formed as particulate materials directly from ash case of coal, trace metal contained in heavy oil with
content, which is originally contained in coal and also a low boiling point is concentrated into fine parti-
includes some unburned carbon. Particularly, almost cles and discharged. Also in the case of the com-
all large-size particles are considered to be this type bustion of liquefied natural gas, carbon particles
of particle. On the other hand, fine particles include formed in the gas phase are generated, albeit in
two types. One type is formed in the process by which trace amounts.
low boiling point metal contained in coal ash is In contrast, only in the case of diesel engines, fuel
evaporated and vaporized in a high-temperature com- is injected into the high-temperature and high-
bustion field and then becomes particles in the pressure atmosphere produced by compressing only
exhaust gas cooling process. The other includes car- air to induce spontaneous ignition, and combustion
bon particles formed in the gas phase, or so-called continues with a heterogeneous mixture of fuel and
soot, which is generated due to the delay in oxygen air in the combustion chamber. Therefore, particulate
supply for combustion of evaporated volatile matter materials mainly consisting of unburnt carbon are
in the initial stage. generated due to incomplete combustion.
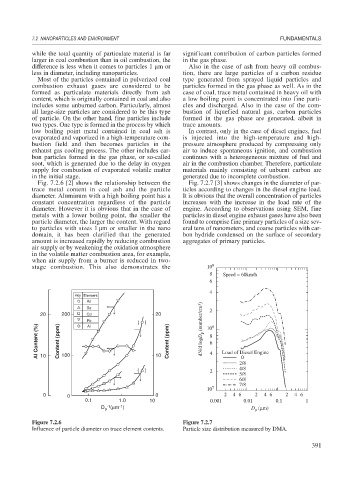
Fig. 7.2.6 [2] shows the relationship between the Fig. 7.2.7 [3] shows changes in the diameter of par-
trace metal content in coal ash and the particle ticles according to changes in the diesel engine load.
diameter. Aluminum with a high boiling point has a It is obvious that the overall concentration of particles
constant concentration regardless of the particle increases with the increase in the load rate of the
diameter. However it is obvious that in the case of engine. According to observations using SEM, fine
metals with a lower boiling point, the smaller the particles in diesel engine exhaust gases have also been
particle diameter, the larger the content. With regard found to comprise fine primary particles of a size sev-
to particles with sizes 1 m or smaller in the nano eral tens of nanometers, and coarse particles with car-
domain, it has been clarified that the generated bon hydride condensed on the surface of secondary
amount is increased rapidly by reducing combustion aggregates of primary particles.
air supply or by weakening the oxidation atmosphere
in the volatile matter combustion area, for example,
when air supply from a burner is reduced in two-
stage combustion. This also demonstrates the 10 9
8 Speed = 60km/h
6
4
key Element
As
Se 2
20 200 Cd 20
Pb ( ) dN/d logD p (number/cm 3 ) 10 8
Al Content (%) Content (ppm) Content (ppm) 6 8
Al
Load of Diesel Engine
4
100
10
10
0
2/8
( ) 2 4/8
5/8
6/8
7/8
10 7
0 0 0 2 4 6 2 4 6 2 4 6
0.1 1.0 10 0.001 0.01 0.1 1
-1
D p (μm -1 ) D p (μm)
Figure 7.2.6 Figure 7.2.7
Influence of particle diameter on trace element contents. Particle size distribution measured by DMA.
391