Page 212 - Neural Network Modeling and Identification of Dynamical Systems
P. 212
6.2 SEMIEMPIRICAL MODELING OF LONGITUDINAL SHORT-PERIOD MOTION FOR A MANEUVERABLE AIRCRAFT 203
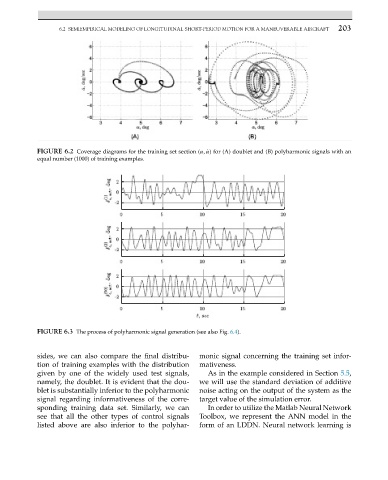
FIGURE 6.2 Coverage diagrams for the training set section (α, ˙α) for (A) doublet and (B) polyharmonic signals with an
equal number (1000) of training examples.
FIGURE 6.3 The process of polyharmonic signal generation (see also Fig. 6.4).
sides, we can also compare the final distribu- monic signal concerning the training set infor-
tion of training examples with the distribution mativeness.
given by one of the widely used test signals, As in the example considered in Section 5.5,
namely, the doublet. It is evident that the dou- we will use the standard deviation of additive
blet is substantially inferior to the polyharmonic noise acting on the output of the system as the
signal regarding informativeness of the corre- target value of the simulation error.
sponding training data set. Similarly, we can In order to utilize the Matlab Neural Network
see that all the other types of control signals Toolbox, we represent the ANN model in the
listed above are also inferior to the polyhar- form of an LDDN. Neural network learning is