Page 63 - Neural Network Modeling and Identification of Dynamical Systems
P. 63
2.2 ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORK TRAINING METHODS 51
(r,p) (p,q)
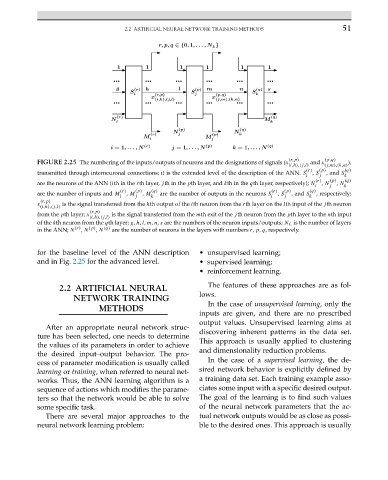
FIGURE 2.25 The numbering of the inputs/outputs of neurons and the designations of signals (x and x ),
(i,h),(j,l) (j,m),(k,n)
(r) (p) (q)
transmitted through interneuronal connections; it is the extended level of the description of the ANN. S , S ,and S
i j k
(r) (p) (q)
are the neurons of the ANN (ith in the rth layer, jth in the pth layer, and kth in the qth layer, respectively); N , N , N
i j k
(r) (p) (q) (r) (p) (q)
are the number of inputs and M , M , M are the number of outputs in the neurons S , S ,and S , respectively;
i j k i j k
(r,p)
x is the signal transferred from the hth output of the ith neuron from the rth layer on the lth input of the jth neuron
(i,h),(j,l)
(r,p)
from the pth layer; x is the signal transferred from the mth exit of the jth neuron from the pth layer to the nth input
(i,h),(j,l)
of the kth neuron from the qth layer; g, h, l, m, n, s are the numbers of the neuron inputs/outputs; N L is the number of layers
in the ANN; N (r) , N (p) , N (q) are the number of neurons in the layers with numbers r, p, q, respectively.
for the baseline level of the ANN description • unsupervised learning;
and in Fig. 2.25 for the advanced level. • supervised learning;
• reinforcement learning.
2.2 ARTIFICIAL NEURAL The features of these approaches are as fol-
lows.
NETWORK TRAINING
METHODS In the case of unsupervised learning, only the
inputs are given, and there are no prescribed
output values. Unsupervised learning aims at
After an appropriate neural network struc-
discovering inherent patterns in the data set.
ture has been selected, one needs to determine
This approach is usually applied to clustering
the values of its parameters in order to achieve
and dimensionality reduction problems.
the desired input–output behavior. The pro-
cess of parameter modification is usually called In the case of a supervised learning,thede-
learning or training, when referred to neural net- sired network behavior is explicitly defined by
works. Thus, the ANN learning algorithm is a a training data set. Each training example asso-
sequence of actions which modifies the parame- ciates some input with a specific desired output.
ters so that the network would be able to solve The goal of the learning is to find such values
some specific task. of the neural network parameters that the ac-
There are several major approaches to the tual network outputs would be as close as possi-
neural network learning problem: ble to the desired ones. This approach is usually