Page 62 - Neural Network Modeling and Identification of Dynamical Systems
P. 62
50 2. DYNAMIC NEURAL NETWORKS: STRUCTURES AND TRAINING METHODS
(r,p) (p,q)
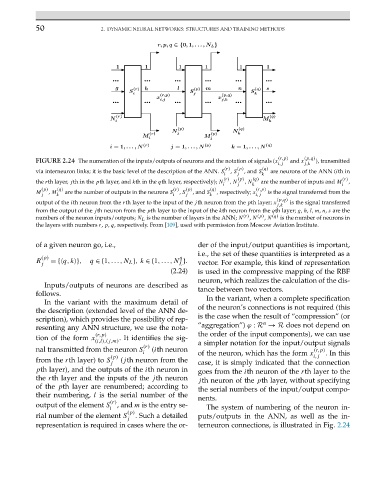
FIGURE 2.24 The numeration of the inputs/outputs of neurons and the notation of signals (x and x ), transmitted
i,j j,k
(r) (p) (q)
via interneuron links; it is the basic level of the description of the ANN. S , S ,and S areneurons of theANN(ith in
i j k
(r) (p) (q) (r)
the rth layer, jth in the pth layer, and kth in the qth layer, respectively); N , N , N are the number of inputs and M ,
i j k i
(p) (q) (r) (p) (q) (r,p)
M , M are the number of outputs in the neurons S , S ,and S , respectively; x is the signal transferred from the
j k i j k i,j
(p,q)
output of the ith neuron from the rth layer to the input of the jth neuron from the pth layer; x is the signal transferred
j,k
from the output of the jth neuron from the pth layer to the input of the kth neuron from the qth layer; g, h, l, m, n, s are the
numbers of the neuron inputs/outputs; N L is the number of layers in the ANN; N (r) , N (p) , N (q) is the number of neurons in
thelayerswithnumbers r, p, q, respectively. From [109], used with permission from Moscow Aviation Institute.
of a given neuron go, i.e., der of the input/output quantities is important,
i.e., the set of these quantities is interpreted as a
(p) q
R ={ q,k }, q ∈{1,...,N L },k ∈{1,...,N }.
j L vector. For example, this kind of representation
(2.24) is used in the compressive mapping of the RBF
neuron, which realizes the calculation of the dis-
Inputs/outputs of neurons are described as
follows. tance between two vectors.
In the variant with the maximum detail of In the variant, when a complete specification
of the neuron’s connections is not required (this
the description (extended level of the ANN de-
scription), which provides the possibility of rep- is the case when the result of “compression” (or
n
resenting any ANN structure, we use the nota- “aggregation”) ϕ : R → R does not depend on
(r,p) the order of the input components), we can use
tion of the form x . It identifies the sig-
(i,l),(j,m) a simpler notation for the input/output signals
(r)
nal transmitted from the neuron S (ith neuron (r,p)
i of the neuron, which has the form x .Inthis
(p) i,j
from the rth layer) to S (jth neuron from the
j case, it is simply indicated that the connection
pth layer), and the outputs of the ith neuron in goes from the ith neuron of the rth layer to the
the rth layer and the inputs of the jth neuron jth neuron of the pth layer, without specifying
of the pth layer are renumbered; according to
the serial numbers of the input/output compo-
their numbering, l is the serial number of the nents.
(r)
output of the element S ,and m is the entry se-
i The system of numbering of the neuron in-
(p)
rial number of the element S . Such a detailed puts/outputs in the ANN, as well as the in-
j
representation is required in cases where the or- terneuron connections, is illustrated in Fig. 2.24