Page 61 - Neural Network Modeling and Identification of Dynamical Systems
P. 61
2.1 ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORK STRUCTURES 49
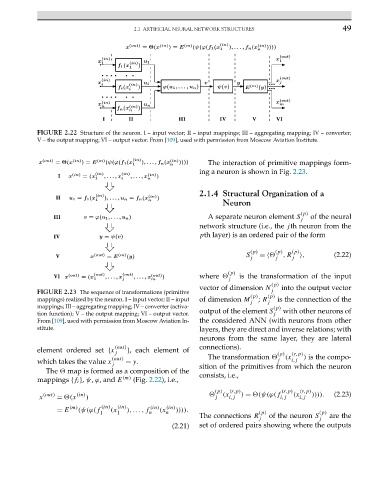
FIGURE 2.22 Structure of the neuron. I – input vector; II – input mappings; III – aggregating mapping; IV – converter;
V – the output mapping; VI – output vector. From [109], used with permission from Moscow Aviation Institute.
The interaction of primitive mappings form-
ing a neuron is shown in Fig. 2.23.
2.1.4 Structural Organization of a
Neuron
(p)
A separate neuron element S of the neural
j
network structure (i.e., the jth neuron from the
pth layer) is an ordered pair of the form
(p) (p) (p)
S = ,R , (2.22)
j j j
(p)
where is the transformation of the input
j
(p)
vector of dimension N into the output vector
FIGURE 2.23 The sequence of transformations (primitive j
(p) (p)
mappings) realized by the neuron. I – input vector; II – input of dimension M j ; R j is the connection of the
mappings; III – aggregating mapping; IV – converter (activa- (p)
tion function); V – the output mapping; VI – output vector. output of the element S j with other neurons of
From [109], used with permission from Moscow Aviation In- the considered ANN (with neurons from other
stitute. layers, they are direct and inverse relations; with
neurons from the same layer, they are lateral
(out) connections).
element ordered set {x }, each element of
j (p) (r,p)
(out) The transformation j (x i,j ) is the compo-
which takes the value x = y.
j sition of the primitives from which the neuron
The map is formed as a composition of the consists, i.e.,
mappings {f i }, ψ, ϕ,and E (m) (Fig. 2.22), i.e.,
(p) (r,p) (r,p) (r,p)
x (out) = (x (in) ) j (x i,j ) = (ψ(ϕ(f i,j (x i,j )))). (2.23)
(m) (in) (in) (in) (in)
= E (ψ(ϕ(f (x ),...,f (x )))).
1 1 n n (p) (p)
The connections R of the neuron S are the
j j
(2.21) set of ordered pairs showing where the outputs