Page 148 - New Trends In Coal Conversion
P. 148
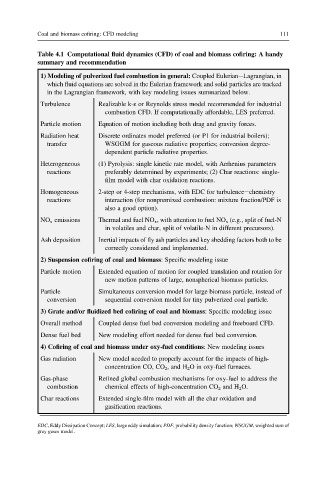
Coal and biomass cofiring: CFD modeling 111
Table 4.1 Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) of coal and biomass cofiring: A handy
summary and recommendation
1) Modeling of pulverized fuel combustion in general: Coupled EulerianeLagrangian, in
which fluid equations are solved in the Eulerian framework and solid particles are tracked
in the Lagrangian framework, with key modeling issues summarized below.
Turbulence Realizable k-ε or Reynolds stress model recommended for industrial
combustion CFD. If computationally affordable, LES preferred.
Particle motion Equation of motion including both drag and gravity forces.
Radiation heat Discrete ordinates model preferred (or P1 for industrial boilers);
transfer WSGGM for gaseous radiative properties; conversion degree-
dependent particle radiative properties.
Heterogeneous (1) Pyrolysis: single kinetic rate model, with Arrhenius parameters
reactions preferably determined by experiments; (2) Char reactions: single-
film model with char oxidation reactions.
Homogeneous 2-step or 4-step mechanisms, with EDC for turbulenceechemistry
reactions interaction (for nonpremixed combustion: mixture fraction/PDF is
also a good option).
NO x emissions Thermal and fuel NO x , with attention to fuel NO x (e.g., split of fuel-N
in volatiles and char, split of volatile-N in different precursors).
Ash deposition Inertial impacts of fly ash particles and key shedding factors both to be
correctly considered and implemented.
2) Suspension cofiring of coal and biomass: Specific modeling issue
Particle motion Extended equation of motion for coupled translation and rotation for
new motion patterns of large, nonspherical biomass particles.
Particle Simultaneous conversion model for large biomass particle, instead of
conversion sequential conversion model for tiny pulverized coal particle.
3) Grate and/or fluidized bed cofiring of coal and biomass: Specific modeling issue
Overall method Coupled dense fuel bed conversion modeling and freeboard CFD.
Dense fuel bed New modeling effort needed for dense fuel bed conversion.
4) Cofiring of coal and biomass under oxy-fuel conditions: New modeling issues
Gas radiation New model needed to properly account for the impacts of high-
concentration CO, CO 2 , and H 2 O in oxy-fuel furnaces.
Gas-phase Refined global combustion mechanisms for oxy-fuel to address the
combustion chemical effects of high-concentration CO 2 and H 2 O.
Char reactions Extended single-film model with all the char oxidation and
gasification reactions.
EDC, Eddy Dissipation Concept; LES, large eddy simulation; PDF, probability density function; WSGGM, weighted sum of
gray gases model.