Page 101 - New Trends in Eco efficient and Recycled Concrete
P. 101
Recycled plastic 75
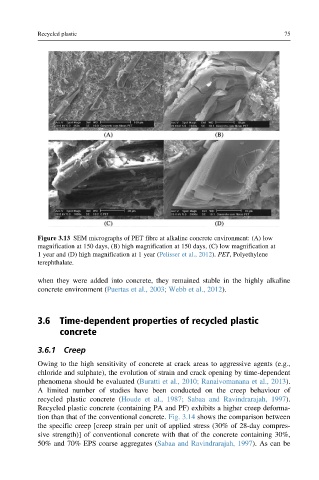
Figure 3.13 SEM micrographs of PET fibre at alkaline concrete environment: (A) low
magnification at 150 days, (B) high magnification at 150 days, (C) low magnification at
1 year and (D) high magnification at 1 year (Pelisser et al., 2012). PET, Polyethylene
terephthalate.
when they were added into concrete, they remained stable in the highly alkaline
concrete environment (Puertas et al., 2003; Webb et al., 2012).
3.6 Time-dependent properties of recycled plastic
concrete
3.6.1 Creep
Owing to the high sensitivity of concrete at crack areas to aggressive agents (e.g.,
chloride and sulphate), the evolution of strain and crack opening by time-dependent
phenomena should be evaluated (Buratti et al., 2010; Ranaivomanana et al., 2013).
A limited number of studies have been conducted on the creep behaviour of
recycled plastic concrete (Houde et al., 1987; Sabaa and Ravindrarajah, 1997).
Recycled plastic concrete (containing PA and PF) exhibits a higher creep deforma-
tion than that of the conventional concrete. Fig. 3.14 shows the comparison between
the specific creep [creep strain per unit of applied stress (30% of 28-day compres-
sive strength)] of conventional concrete with that of the concrete containing 30%,
50% and 70% EPS coarse aggregates (Sabaa and Ravindrarajah, 1997). As can be