Page 222 - New Trends in Eco efficient and Recycled Concrete
P. 222
192 New Trends in Eco-efficient and Recycled Concrete
8.2 Mollusc shells
Various publications on the microscopic and mineralogical composition of different
types of marine shells coincide largely. All the shells are composed mainly of cal-
cium carbonate (CaCO 3 ) in 95% 99% by weight and other oxides in small propor-
tions (potassium, silicon, and iron, etc.) (Mo et al., 2018). Oyster shells have the
most calcium carbonate (up to 98%). The values of loss on ignition is also similar
for the species of green mussel, short-necked clam, oyster and cockle, with values
between 42.2% and 42.8% (Martı ´nez-Garcı ´a et al., 2017). The basic composition of
mollusc shells is similar regardless of the species and they present a percentage of
calcium carbonate above 95% independently of the species (Mo et al., 2018).
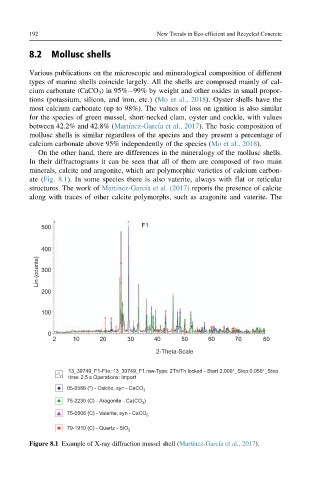
On the other hand, there are differences in the mineralogy of the mollusc shells.
In their diffractograms it can be seen that all of them are composed of two main
minerals, calcite and aragonite, which are polymorphic varieties of calcium carbon-
ate (Fig. 8.1). In some species there is also vaterite, always with flat or reticular
structures. The work of Martı ´nez-Garcı ´a et al. (2017) reports the presence of calcite
along with traces of other calcite polymorphs, such as aragonite and vaterite. The
500 F1
400
Lin (counts) 300
200
100
0
2 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
2-Theta-Scale
13_30749_F1-File: 13_30749_F1.raw-Type: 2Th/Th locked - Start 2,000°_Step:0.050°_Step
time: 2.5 s Operations: Import
05-0586 (*) - Calcite, syn - CaCO 3
75-2230 (C) - Aragonite - Ca(CO )
3
75-0506 (C) - Vaterite, syn - CaCO 3
79-1910 (C) - Quartz - SiO 2
Figure 8.1 Example of X-ray diffraction mussel shell (Martı ´nez-Garcı ´a et al., 2017).