Page 365 - New Trends in Eco efficient and Recycled Concrete
P. 365
320 New Trends in Eco-efficient and Recycled Concrete
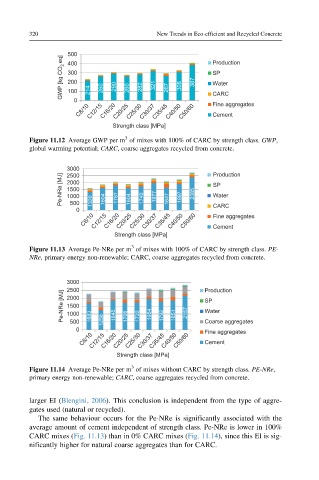
500 Production
GWP [kg CO 2 eq] 300 214 260 290 260 282 321 267 308 387 SP
400
200
Water
100
CARC
0
C8/10 C12/15 C16/20 C20/25 C25/30 C30/37 C35/45 C40/50 C50/60 Fine aggregates
Cement
Strength class [MPa]
3
Figure 11.12 Average GWP per m of mixes with 100% of CARC by strength class. GWP,
global warming potential; CARC, coarse aggregates recycled from concrete.
3000 Production
Pe-NRe [MJ] 2000 1604 1787 1604 1740 1977 1647 1897 2385 SP
2500
1500
Water
1000
500
0 1320 CARC
C8/10 C12/15 C16/20 C20/25 C25/30 C30/37 C35/45 C40/50 C50/60 Fine aggregates
Cement
Strength class [MPa]
3
Figure 11.13 Average Pe-NRe per m of mixes with 100% of CARC by strength class. PE-
NRe, primary energy non-renewable; CARC, coarse aggregates recycled from concrete.
3000 Production
2500
Pe-NRe [MJ] 2000 1683 1845 1706 1720 1954 1792 1851 2157 SP
1500
Water
1000
500
0 1256 Coarse aggregates
Fine aggregates
C8/10 C12/15 C16/20 C20/25 C25/30 C30/37 C35/45 C40/50 C50/60 Cement
Strength class [MPa]
3
Figure 11.14 Average Pe-NRe per m of mixes without CARC by strength class. PE-NRe,
primary energy non-renewable; CARC, coarse aggregates recycled from concrete.
larger EI (Blengini, 2006). This conclusion is independent from the type of aggre-
gates used (natural or recycled).
The same behaviour occurs for the Pe-NRe is significantly associated with the
average amount of cement independent of strength class. Pe-NRe is lower in 100%
CARC mixes (Fig. 11.13) than in 0% CARC mixes (Fig. 11.14), since this EI is sig-
nificantly higher for natural coarse aggregates than for CARC.