Page 455 - New Trends in Eco efficient and Recycled Concrete
P. 455
Application of alkali-activated industrial waste 405
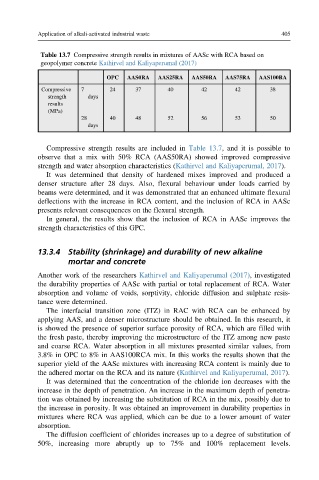
Table 13.7 Compressive strength results in mixtures of AASc with RCA based on
geopolymer concrete Kathirvel and Kaliyaperumal (2017)
OPC AAS0RA AAS25RA AAS50RA AAS75RA AAS100RA
Compressive 7 24 37 40 42 42 38
strength days
results
(MPa)
28 40 48 52 56 53 50
days
Compressive strength results are included in Table 13.7, and it is possible to
observe that a mix with 50% RCA (AAS50RA) showed improved compressive
strength and water absorption characteristics (Kathirvel and Kaliyaperumal, 2017).
It was determined that density of hardened mixes improved and produced a
denser structure after 28 days. Also, flexural behaviour under loads carried by
beams were determined, and it was demonstrated that an enhanced ultimate flexural
deflections with the increase in RCA content, and the inclusion of RCA in AASc
presents relevant consequences on the flexural strength.
In general, the results show that the inclusion of RCA in AASc improves the
strength characteristics of this GPC.
13.3.4 Stability (shrinkage) and durability of new alkaline
mortar and concrete
Another work of the researchers Kathirvel and Kaliyaperumal (2017), investigated
the durability properties of AASc with partial or total replacement of RCA. Water
absorption and volume of voids, sorptivity, chloride diffusion and sulphate resis-
tance were determined.
The interfacial transition zone (ITZ) in RAC with RCA can be enhanced by
applying AAS, and a denser microstructure should be obtained. In this research, it
is showed the presence of superior surface porosity of RCA, which are filled with
the fresh paste, thereby improving the microstructure of the ITZ among new paste
and coarse RCA. Water absorption in all mixtures presented similar values, from
3.8% in OPC to 8% in AAS100RCA mix. In this works the results shown that the
superior yield of the AASc mixtures with increasing RCA content is mainly due to
the adhered mortar on the RCA and its nature (Kathirvel and Kaliyaperumal, 2017).
It was determined that the concentration of the chloride ion decreases with the
increase in the depth of penetration. An increase in the maximum depth of penetra-
tion was obtained by increasing the substitution of RCA in the mix, possibly due to
the increase in porosity. It was obtained an improvement in durability properties in
mixtures where RCA was applied, which can be due to a lower amount of water
absorption.
The diffusion coefficient of chlorides increases up to a degree of substitution of
50%, increasing more abruptly up to 75% and 100% replacement levels.