Page 147 - Numerical Analysis Using MATLAB and Excel
P. 147
Solution of Simultaneous Equations with Matrices
1 –
2. Next, we compute and display the inverse of R, that is, R . We choose B7:D9 for the elements
of this inverted matrix. We format this block for number display with three decimal places.
With this range highlighted and making sure that the cell marker is in B7, we type the formula
=MININVERSE(B3:D5)
and we press the Crtl−Shift−Enter keys simultaneously. We observe that R 1 – appears in these
cells.
3. Now, we choose the block of cells G7:G9 for the values of the current . As before, we high-
I
light them, and with the cell marker positioned in G7, we type the formula
=MMULT(B7:D9,G3:G5)
and we press the Crtl−Shift−Enter keys simultaneously. The values of I then appear in G7:G9.
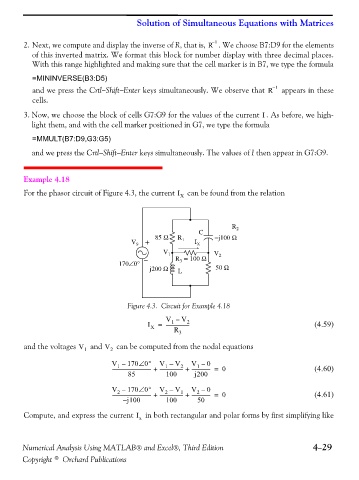
Example 4.18
For the phasor circuit of Figure 4.3, the current I X can be found from the relation
R 2
C
85 Ω R −j100 Ω
+ 1
V S I X
V 1 V 2
− R = 100 Ω
3
170∠0°
j200 Ω L 50 Ω
Figure 4.3. Circuit for Example 4.18
V – V
1
I X = ------------------- 2 (4.59)
R
3
and the voltages V 1 and V 2 can be computed from the nodal equations
∠
V – 170 0° V – V V – 0
1
2
1
1
-------------------------------- + ------------------- + --------------- = 0 (4.60)
85 100 j200
∠
V – 170 0° V – V V – 0
1
2
2
2
-------------------------------- + ------------------- + --------------- = 0 (4.61)
– j100 100 50
Compute, and express the current in both rectangular and polar forms by first simplifying like
I
x
Numerical Analysis Using MATLAB® and Excel®, Third Edition 4−29
Copyright © Orchard Publications