Page 145 - Numerical Analysis Using MATLAB and Excel
P. 145
Solution of Simultaneous Equations with Matrices
Example 4.17
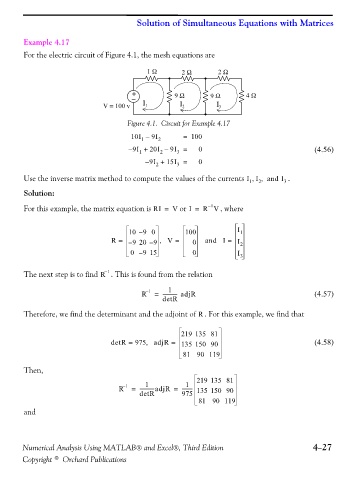
For the electric circuit of Figure 4.1, the mesh equations are
1 Ω 2 Ω 2 Ω
+ 9 Ω 9 Ω 4 Ω
−
V = 100 v I 1 I 2 I 3
Figure 4.1. Circuit for Example 4.17
10I – 9I = 100
1 2
– 9I + 20I – 9I = 0 (4.56)
2
1
3
– 9I + 15I = 0
2
3
Use the inverse matrix method to compute the values of the currents I I and I,, 3 .
2
1
Solution:
1 –
For this example, the matrix equation is RI = V or I = R V , where
–
10 9 0 100 I 1
R = – 9 20 9 , V = 0 and I = I 2
–
9
0 – 15 0 I 3
The next step is to find R 1 – . This is found from the relation
1
R 1 – = ------------ adjR (4.57)
detR
Therefore, we find the determinant and the adjoint of . For this example, we find that
R
219 135 81
detR = 975 adjR =, 135 150 90 (4.58)
81 90 119
Then,
219 135 81
1
1
R 1 – = ------------adjR = --------- 135 150 90
detR 975
81 90 119
and
Numerical Analysis Using MATLAB® and Excel®, Third Edition 4−27
Copyright © Orchard Publications