Page 235 - Numerical Analysis Using MATLAB and Excel
P. 235
Chapter 6 Fourier, Taylor, and Maclaurin Series
2 π A 2A π 2A 1 t ⎞ π
⎛
2∫
-
b = --- ∫ 0 ----tsin nt t = ------- 0 tsin nt t = ------- ----- sin nt – -- cos nt ⎠
d
d
π ⎝
n
π
π
π
n
n
2
2
2A π 2A 0 (6.37)
= ----------- sin( nt – ntcos nt ) = ----------- sin( nπ – nπcos nπ )
n π 0 n π
2 2
2 2
We observe that:
1.If n = even , sin nπ = 0 and cos nπ = 1 . Then, (6.37) reduces to
2A
)
b = ----------- –( n π nπ = – 2A
-------
n
nπ
2 2
that is, the even harmonics have negative coefficients.
2. If n = odd , sin nπ = , 0 cos nπ = – 1 . Then,
b = ----------- nπ( 2A ) = 2A
-------
n
nπ
n π
2 2
that is, the odd harmonics have positive coefficients.
Thus, the trigonometric Fourier series for the sawtooth waveform with odd symmetry is
2A ⎛ 1 1 1 ⎞ 2A n – 1
1
-
-
-
-
ft() = ------- sin ωt – -- sin 2ωt + -- sin 3ωt – -- sin 4ωt + … = ------- ∑ – ( 1 ) -- sin nωt (6.38)
π ⎝ 2 3 4 ⎠ π n
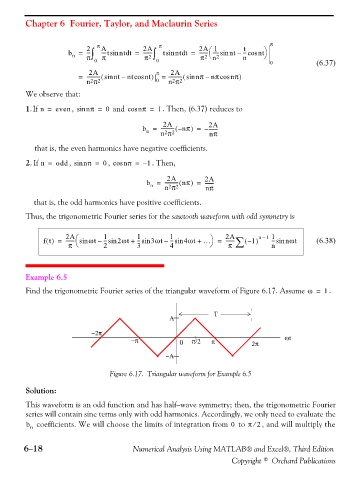
Example 6.5
Find the trigonometric Fourier series of the triangular waveform of Figure 6.17. Assume ω = . 1
T
A
−2π
−π 0 π/2 π 2π ωt
−A
Figure 6.17. Triangular waveform for Example 6.5
Solution:
This waveform is an odd function and has half−wave symmetry; then, the trigonometric Fourier
series will contain sine terms only with odd harmonics. Accordingly, we only need to evaluate the
b n coefficients. We will choose the limits of integration from to π 2⁄ , and will multiply the
0
6−18 Numerical Analysis Using MATLAB® and Excel®, Third Edition
Copyright © Orchard Publications