Page 134 - Open-Hole Log Analysis and Formation Evaluation
P. 134
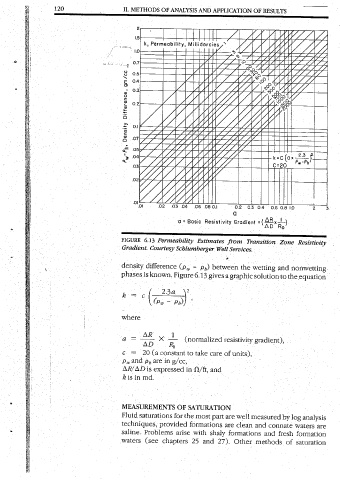
Pw-Ph, Density Difference, gm/cc IL 120
c
Py
: phases ‘density ‘Gradient. FIGURE ° 29:9
x © b k, 2 METHODS
=
k=
Fluid
Risin
where
saline.
waters
and
€
AR/AD
is
20
p,
is
AD
AR:
md.
az AR
6.13
techniques,
(a
(see
(Zz
are
x
in
known.
Problems
saturations
MEASUREMENTS
Ry
difference
i
for
expressed
constant
g/cc,
OF
provided
chapters
arise
, 7 =) TT > \? 23a (p,, - ,) Courtesy Schlumberger Estimates Permeability a= Basic Resistivity y _ . Permeability, Millidarcies AND OF ANALYSIS
the
to
25
with
take
in-0/ft,
most
and
and
formations
(normalized
part
shaly
27).
SATURATION
are
: resistivity Figure 6.13 gives a graphic solution to the between ¢ Well Services. from Transition Gradient . ge a 0.2 03 04° »» OF APPLICATION
are well
care of units),
Other
clean
formations
and
. gradient), the equation and wetting Zone Resistivity Ro! (A5 =(22x—' 1 AR, 08 10 2 06 RESULTS 121
and
measured
methods
by
connate
fresh
of
log
waters
analysis
nonwetting
saturation
are
formation
a
is
as
the
a
and
of a
and
and
good
found
water,
rock
FIGURE
system
several
finding
“pores”
chapter
the
Many
case
Connate
in
to
solution.
for
2.
of
Chapter
6.14
properties
X,,.
qualitative
are
their length
techniques
porous
parallel
To
conductivity
the
O-m
flow
24
experimental
resistivity
determination
starting
where
waters
is
proportional
of
of
water-filled
(see
Here,
of wet
conduct
to
pore
is Z, we
an
are
logs,
it
Water Resistivity
system,
similarities
example,
measure
both
a
is
cylindrical
range
R,,
between
and
point
rocks.
find water
can
R,;
oil
of
electric
in
can
exist
depending
since
spaces.
Rock
chapters
oil
dedicated
for
Simplified Model
observations
value
be
tubes
filled with water
available
4
electricity
(Z/A).
on
is
relative
is
oil-bearing
both
and
If
estimate
current
necessary
Matrix
of R,,
the
saturation
Figure
the
and
oil-bearing
resistivity
and water
from
between
is
the
due
gas
drilled
equated
by
sand.
are
6.14
26).
exclusively
the
following
only to
depend
from
rocks
area
salinity
through
with
to
a
proper
A
on
. Connate Water with Pore Filled SYSTEMS 6. THE PHYSICS OF ROCK/FLUID
electrical
flow
entirely
the
Mud
permeability
was
through
is
of resistivity R,,,
required.
the
the
about
shows
present
to
of Water-Filled Rock
of
to
and
ee
it.
a
rock.
saturations,
in
coring
a
their
If
the
as
understand
Investigation
,
small,
1/100
The
fluids
logging
behavior
cube
water
System.
and
of
we
pore
methods
total
electrical
that
ions
pioneered
of
the resistivity ofthe total
of
these
can
of an
there
in
the
interconnected
development
area
is
temperature
rock
the
is
a
a
ability
with
small
cylindrical
rock system
Aand
water
electrical
for
a
in
his
quantitative analysis of porosity
of
rock
| available of the - to Q-m up electrolytes of by Archie: A the and electrical there system pores, In conductivity to permeability through seen have provide a analysis core