Page 13 - Optical Communications Essentials
P. 13
Basic Concepts of Communication Systems
Basic Concepts of Communication Systems 3
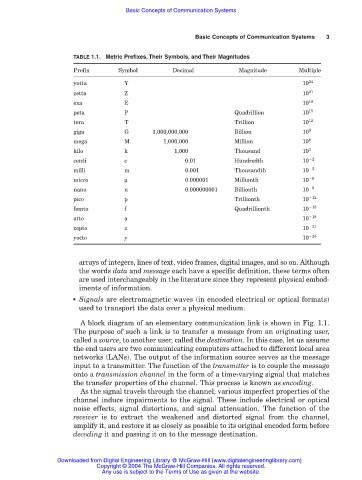
TABLE 1.1. Metric Prefixes, Their Symbols, and Their Magnitudes
Prefix Symbol Decimal Magnitude Multiple
yotta Y 10 24
zetta Z 10 21
exa E 10 18
peta P Quadrillion 10 15
tera T Trillion 10 12
giga G 1,000,000,000 Billion 10 9
mega M 1,000,000 Million 10 6
kilo k 1,000 Thousand 10 3
centi c 0.01 Hundredth 10 2
milli m 0.001 Thousandth 10 3
micro µ 0.000001 Millionth 10 6
nano n 0.000000001 Billionth 10 9
pico p Trillionth 10 12
femto f Quadrillionth 10 15
atto a 10 18
zepto z 10 21
yocto y 10 24
arrays of integers, lines of text, video frames, digital images, and so on. Although
the words data and message each have a specific definition, these terms often
are used interchangeably in the literature since they represent physical embod-
iments of information.
■ Signals are electromagnetic waves (in encoded electrical or optical formats)
used to transport the data over a physical medium.
A block diagram of an elementary communication link is shown in Fig. 1.1.
The purpose of such a link is to transfer a message from an originating user,
called a source, to another user, called the destination. In this case, let us assume
the end users are two communicating computers attached to different local area
networks (LANs). The output of the information source serves as the message
input to a transmitter. The function of the transmitter is to couple the message
onto a transmission channel in the form of a time-varying signal that matches
the transfer properties of the channel. This process is known as encoding.
As the signal travels through the channel, various imperfect properties of the
channel induce impairments to the signal. These include electrical or optical
noise effects, signal distortions, and signal attenuation. The function of the
receiver is to extract the weakened and distorted signal from the channel,
amplify it, and restore it as closely as possible to its original encoded form before
decoding it and passing it on to the message destination.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.