Page 186 - Optical Communications Essentials
P. 186
Optical Amplifiers
176 Chapter Eleven
11.1. Basic Applications
Optical amplifiers have found widespread use not only in long-distance, point-
to-point optical fiber links, but also in multiaccess networks (where an optical
signal is divided among many users) to compensate for signal-splitting losses.
The features of optical amplifiers have led to many diverse applications, each
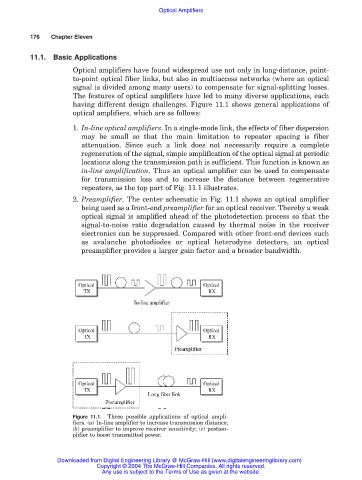
having different design challenges. Figure 11.1 shows general applications of
optical amplifiers, which are as follows:
1. In-line optical amplifiers. In a single-mode link, the effects of fiber dispersion
may be small so that the main limitation to repeater spacing is fiber
attenuation. Since such a link does not necessarily require a complete
regeneration of the signal, simple amplification of the optical signal at periodic
locations along the transmission path is sufficient. This function is known as
in-line amplification. Thus an optical amplifier can be used to compensate
for transmission loss and to increase the distance between regenerative
repeaters, as the top part of Fig. 11.1 illustrates.
2. Preamplifier. The center schematic in Fig. 11.1 shows an optical amplifier
being used as a front-end preamplifier for an optical receiver. Thereby a weak
optical signal is amplified ahead of the photodetection process so that the
signal-to-noise ratio degradation caused by thermal noise in the receiver
electronics can be suppressed. Compared with other front-end devices such
as avalanche photodiodes or optical heterodyne detectors, an optical
preamplifier provides a larger gain factor and a broader bandwidth.
Figure 11.1. Three possible applications of optical ampli-
fiers. (a) In-line amplifier to increase transmission distance;
(b) preamplifier to improve receiver sensitivity; (c) postam-
plifier to boost transmitted power.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.