Page 336 - Optical Communications Essentials
P. 336
Test and Measurement
326 Chapter Nineteen
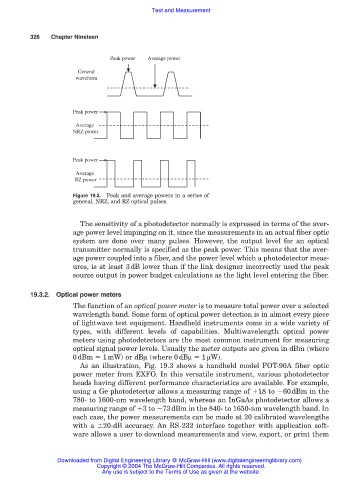
Peak power Average power
General
waveform
Peak power
Average
NRZ power
Peak power
Average
RZ power
Figure 19.2. Peak and average powers in a series of
general, NRZ, and RZ optical pulses.
The sensitivity of a photodetector normally is expressed in terms of the aver-
age power level impinging on it, since the measurements in an actual fiber optic
system are done over many pulses. However, the output level for an optical
transmitter normally is specified as the peak power. This means that the aver-
age power coupled into a fiber, and the power level which a photodetector meas-
ures, is at least 3dB lower than if the link designer incorrectly used the peak
source output in power budget calculations as the light level entering the fiber.
19.3.2. Optical power meters
The function of an optical power meter is to measure total power over a selected
wavelength band. Some form of optical power detection is in almost every piece
of lightwave test equipment. Handheld instruments come in a wide variety of
types, with different levels of capabilities. Multiwavelength optical power
meters using photodetectors are the most common instrument for measuring
optical signal power levels. Usually the meter outputs are given in dBm (where
0dBm 1mW) or dBµ (where 0dBµ 1µW).
As an illustration, Fig. 19.3 shows a handheld model FOT-90A fiber optic
power meter from EXFO. In this versatile instrument, various photodetector
heads having different performance characteristics are available. For example,
using a Ge photodetector allows a measuring range of 18 to 60dBm in the
780- to 1600-nm wavelength band, whereas an InGaAs photodetector allows a
measuring range of 3to 73dBm in the 840- to 1650-nm wavelength band. In
each case, the power measurements can be made at 20 calibrated wavelengths
with a 20-dB accuracy. An RS-232 interface together with application soft-
ware allows a user to download measurements and view, export, or print them
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.