Page 241 - Optofluidics Fundamentals, Devices, and Applications
P. 241
216 Cha pte r Ni ne
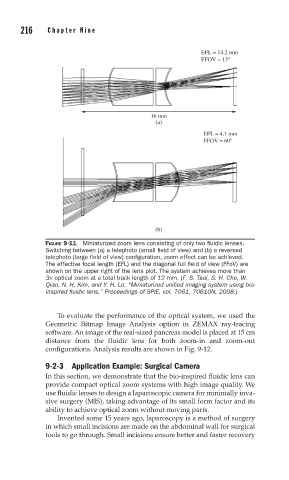
EFL = 14.2 mm
FFOV = 13°
16 mm
(a)
EFL = 4.1 mm
FFOV = 60°
(b)
FIGURE 9-11 Miniaturized zoom lens consisting of only two fl uidic lenses.
Switching between (a) a telephoto (small fi eld of view) and (b) a reversed
telephoto (large fi eld of view) confi guration, zoom effect can be achieved.
The effective focal length (EFL) and the diagonal full fi eld of view (FFoV) are
shown on the upper right of the lens plot. The system achieves more than
3× optical zoom at a total track length of 12 mm. (F. S. Tsai, S. H. Cho, W.
Qiao, N. H. Kim, and Y. H. Lo, “Miniaturized unifi ed imaging system using bio-
inspired fl uidic lens,” Proceedings of SPIE, vol. 7061, 70610N, 2008.)
To evaluate the performance of the optical system, we used the
Geometric Bitmap Image Analysis option in ZEMAX ray-tracing
software. An image of the real-sized pancreas model is placed at 15 cm
distance from the fluidic lens for both zoom-in and zoom-out
configurations. Analysis results are shown in Fig. 9-12.
9-2-3 Application Example: Surgical Camera
In this section, we demonstrate that the bio-inspired fluidic lens can
provide compact optical zoom systems with high image quality. We
use fluidic lenses to design a laparoscopic camera for minimally inva-
sive surgery (MIS), taking advantage of its small form factor and its
ability to achieve optical zoom without moving parts.
Invented some 15 years ago, laparoscopy is a method of surgery
in which small incisions are made on the abdominal wall for surgical
tools to go through. Small incisions ensure better and faster recovery