Page 243 - Optofluidics Fundamentals, Devices, and Applications
P. 243
218 Cha pte r Ni ne
Fluidic lens
Middle zoom
22 mm
(a)
Fluidic lens
Zoom out
(b)
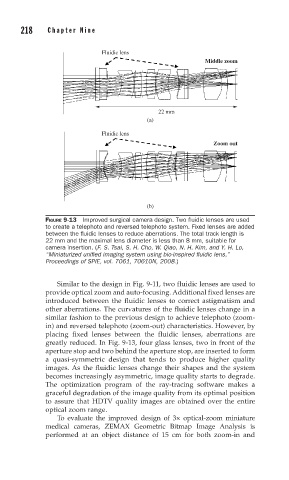
FIGURE 9-13 Improved surgical camera design. Two fl uidic lenses are used
to create a telephoto and reversed telephoto system. Fixed lenses are added
between the fl uidic lenses to reduce aberrations. The total track length is
22 mm and the maximal lens diameter is less than 8 mm, suitable for
camera insertion. (F. S. Tsai, S. H. Cho, W. Qiao, N. H. Kim, and Y. H. Lo,
“Miniaturized unifi ed imaging system using bio-inspired fl uidic lens,”
Proceedings of SPIE, vol. 7061, 70610N, 2008.)
Similar to the design in Fig. 9-11, two fluidic lenses are used to
provide optical zoom and auto-focusing. Additional fixed lenses are
introduced between the fluidic lenses to correct astigmatism and
other aberrations. The curvatures of the fluidic lenses change in a
similar fashion to the previous design to achieve telephoto (zoom-
in) and reversed telephoto (zoom-out) characteristics. However, by
placing fixed lenses between the fluidic lenses, aberrations are
greatly reduced. In Fig. 9-13, four glass lenses, two in front of the
aperture stop and two behind the aperture stop, are inserted to form
a quasi-symmetric design that tends to produce higher quality
images. As the fluidic lenses change their shapes and the system
becomes increasingly asymmetric, image quality starts to degrade.
The optimization program of the ray-tracing software makes a
graceful degradation of the image quality from its optimal position
to assure that HDTV quality images are obtained over the entire
optical zoom range.
To evaluate the improved design of 3× optical-zoom miniature
medical cameras, ZEMAX Geometric Bitmap Image Analysis is
performed at an object distance of 15 cm for both zoom-in and