Page 372 - Organic Electronics in Sensors and Biotechnology
P. 372
Luminescent Conjugated Polymers for Staining and Characterization of Amyloid Deposits 349
sensory performance and the amyloid specificity of LCPs be utilized
in more complex systems such as tissue sections? A couple of studies
have shown that LCPs can be used as amyloid-specific dyes for histo-
logical staining of tissue sections and that LCPs provide additional
information regarding the pathological events of protein aggregation
diseases compared to conventional techniques. 110–112
The proof of the concept of using the LCPs as amyloid-specific
110
dyes in tissue samples was first shown by Nilsson et al. Under cer-
tain conditions PTAA, POMT, and PONT (Fig. 9.1) were shown to
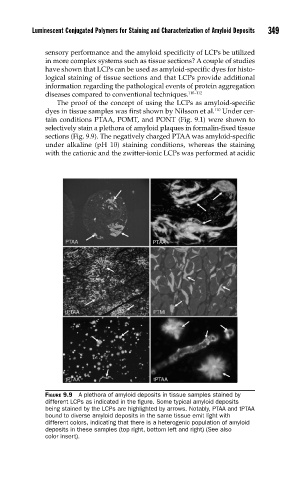
selectively stain a plethora of amyloid plaques in formalin-fixed tissue
sections (Fig. 9.9). The negatively charged PTAA was amyloid-specific
under alkaline (pH 10) staining conditions, whereas the staining
with the cationic and the zwitter-ionic LCPs was performed at acidic
FIGURE 9.9 A plethora of amyloid deposits in tissue samples stained by
different LCPs as indicated in the fi gure. Some typical amyloid deposits
being stained by the LCPs are highlighted by arrows. Notably, PTAA and tPTAA
bound to diverse amyloid deposits in the same tissue emit light with
different colors, indicating that there is a heterogenic population of amyloid
deposits in these samples (top right, bottom left and right) (See also
color insert).