Page 163 - Origin and Prediction of Abnormal Formation Pressures
P. 163
METHODS OF ESTIMATING AND PREDICTING ABNORMAL FORMATION PRESSURES 139
n x (slope)
.05~ -.o56
.054 .----'.05 -
-----'----'.04
.033o
,035
.029 9
, .025
~.0~ .033 . . . . ~5~
.04
[intercept]
\
. I ~ "35 9
9
9 q,.
e'[4 ~ -.01~ ~ 20211,/ /
-.22
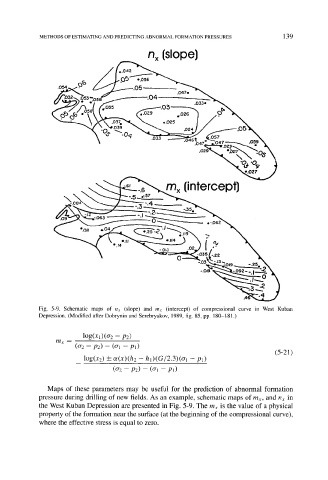
Fig. 5-9. Schematic maps of nx (slope) and mx (intercept) of compressional curve in West Kuban
Depression. (Modified after Dobrynin and Serebryakov, 1989, fig. 85, pp. 180-181.)
log(xl)(o-2 - P2)
mx - (o-2 - P2) - (o-1 - Pl)
(5-21)
log(x2) • ol(x)(h2 -- hI)(G/2.3)(o-I - Pl)
(o-2 -- P2) -- (o-1 Pl)
Maps of these parameters may be useful for the prediction of abnormal formation
pressure during drilling of new fields. As an example, schematic maps of mx, and nx in
the West Kuban Depression are presented in Fig. 5-9. The mx is the value of a physical
property of the formation near the surface (at the beginning of the compressional curve),
where the effective stress is equal to zero.