Page 310 - Origin and Prediction of Abnormal Formation Pressures
P. 310
PORE WATER COMPACTION CHEMISTRY AS RELATED TO OVERPRESSURES 279
Initial Stage / ~ Next stage /
n
f Compaction ~ l ' System requirements
II II II II
~CI ~ Na
il = mll 1. Electroneutrality
mci Na Phase I 9
I
Supernatant mci + x = m I
l'lll'~l" ~ ,,m~-.ll"l. ql~.,ll'l,al'L-all~t 1 J Na
z--.=~_-_z S u s p-e~ ~To~ ---_--_----- S u pe rnat a n t Phase I1'
mll ii
==-X== 4-.:,m C I ~"--~- .m N a~-~ . . . . . . . . . Cl = mNa
1 -=-_---~--_---L C I =_----_---'. ~ N a---_.~ 2. Electrochemical equilibrium
So,Vo =-----------, ---------- ~.E~s~ .~ ~ ~ sTo~ ~---=_---=."
~
=-=- -- -- ----- --. --- -------:.---: ~ . . . . . . . . . . . . = Electrochemical potential
=
:-_ _ _,
..... I II
_ , _ _s
so
i,mci 1- Vo mci - V Electrochemical potential
_ VoXo I II
x -- x o x - V ~Na -- ~Na
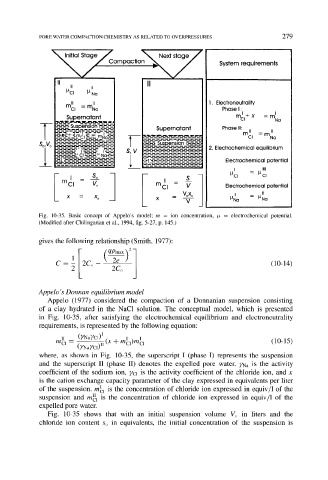
Fig. 10-35. Basic concept of Appelo's model; m = ion concentration, # = electrochemical potential.
(Modified after Chilingarian et al., 1994, fig. 5-27, p. 145.)
gives the following relationship (Smith, 1977)"
( max 1
C-~ 2Co- 2e ) (10-14)
2Co
Appelo's Donnan equilibrium model
Appelo (1977) considered the compaction of a Donnanian suspension consisting
of a clay hydrated in the NaC1 solution. The conceptual model, which is presented
in Fig. 10-35, after satisfying the electrochemical equilibrium and electroneutrality
requirements, is represented by the following equation:
m~l = (VNaYC1)I (X + m~l)m~l (10-15)
(~]NaYC1) II
where, as shown in Fig. 10-35, the superscript I (phase I) represents the suspension
and the superscript II (phase II) denotes the expelled pore water. YNa is the activity
coefficient of the sodium ion, YCl is the activity coefficient of the chloride ion, and x
is the cation exchange capacity parameter of the clay expressed in equivalents per liter
of the suspension, mI1 is the concentration of chloride ion expressed in equiv/1 of the
suspension and m~l is the concentration of chloride ion expressed in equiv/1 of the
expelled pore water.
Fig. 10-35 shows that with an initial suspension volume Vo in liters and the
chloride ion content So in equivalents, the initial concentration of the suspension is