Page 40 - Orlicky's Material Requirements Planning
P. 40
CHAPTER 2 MRP in the Modern World 21
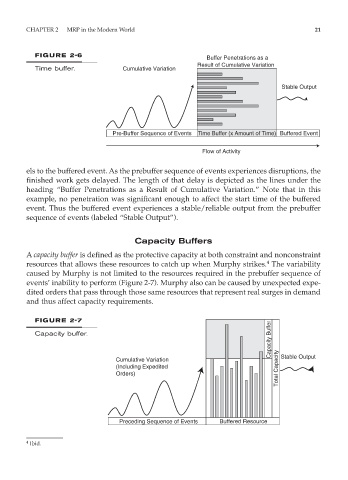
FIGURE 2-6
Buffer Penetrations as a
Result of Cumulative Variation
Time buffer. Cumulative Variation
Stable Output
Pre-Buffer Sequence of Events Time Buffer (x Amount of Time) Buffered Event
Flow of Activity
els to the buffered event. As the prebuffer sequence of events experiences disruptions, the
finished work gets delayed. The length of that delay is depicted as the lines under the
heading “Buffer Penetrations as a Result of Cumulative Variation.” Note that in this
example, no penetration was significant enough to affect the start time of the buffered
event. Thus the buffered event experiences a stable/reliable output from the prebuffer
sequence of events (labeled “Stable Output”).
Capacity Buffers
A capacity buffer is defined as the protective capacity at both constraint and nonconstraint
4
resources that allows these resources to catch up when Murphy strikes. The variability
caused by Murphy is not limited to the resources required in the prebuffer sequence of
events’ inability to perform (Figure 2-7). Murphy also can be caused by unexpected expe-
dited orders that pass through those same resources that represent real surges in demand
and thus affect capacity requirements.
FIGURE 2-7
Capacity Buffer
Capacity buffer.
Cumulative Variation Stable Output
(Including Expedited Total Capacity
Orders)
Preceding Sequence of Events Buffered Resource
4 Ibid.