Page 38 - Orlicky's Material Requirements Planning
P. 38
CHAPTER 2 MRP in the Modern World 19
tomer. However, this is a gross oversimplification and does not represent the weblike net-
work that more accurately reflects a company within its supply chain. Interdependencies
are common. When these interdependencies are subject to variability, the effect is ampli-
fied. The more parts or dependencies there are, the worse is the cumulative effect expe-
rienced by the supply chain and the organizations comprising it. This cumulative effect
is known as the bullwhip effect.
The APICS Dictionary (New York: Blackstone, 2008, p. 15) defines bullwhip effect as:
An extreme change in the supply position upstream in a supply chain generated by a
small change in demand downstream in the supply chain. Inventory can quickly move
from being backordered to being excess. This is caused by the serial nature of commu-
nicating orders up the chain with the inherent transportation delays of moving product
down the chain. The bullwhip effect can be eliminated by synchronizing the supply chain.
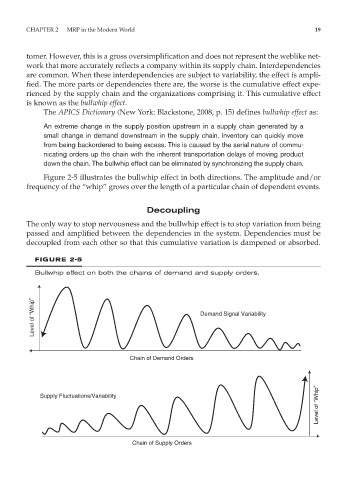
Figure 2-5 illustrates the bullwhip effect in both directions. The amplitude and/or
frequency of the “whip” grows over the length of a particular chain of dependent events.
Decoupling
The only way to stop nervousness and the bullwhip effect is to stop variation from being
passed and amplified between the dependencies in the system. Dependencies must be
decoupled from each other so that this cumulative variation is dampened or absorbed.
FIGURE 2-5
Bullwhip effect on both the chains of demand and supply orders.
Level of “Whip” Demand Signal Variability
Chain of Demand Orders
Level of “Whip”
Supply Fluctuations/Variability
Chain of Supply Orders