Page 147 - PVT Property Correlations
P. 147
124 PVT Property Correlations
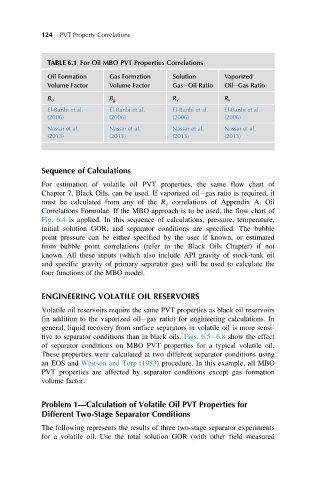
TABLE 6.1 For Oil MBO PVT Properties Correlations
Oil Formation Gas Formation Solution Vaporized
Volume Factor Volume Factor Gas Oil Ratio Oil Gas Ratio
B o
El-Banbi et al.
El-Banbi et al. B g R s R v
El-Banbi et al.
El-Banbi et al.
(2006) (2006) (2006) (2006)
Nassar et al. Nassar et al. Nassar et al. Nassar et al.
(2013) (2013) (2013) (2013)
Sequence of Calculations
For estimation of volatile oil PVT properties, the same flow chart of
Chapter 7, Black Oils, can be used. If vaporized oil gas ratio is required, it
must be calculated from any of the R v correlations of Appendix A, Oil
Correlations Formulae. If the MBO approach is to be used, the flow chart of
Fig. 6.4 is applied. In this sequence of calculations, pressure, temperature,
initial solution GOR, and separator conditions are specified. The bubble
point pressure can be either specified by the user if known, or estimated
from bubble point correlations (refer to the Black Oils Chapter) if not
known. All these inputs (which also include API gravity of stock-tank oil
and specific gravity of primary separator gas) will be used to calculate the
four functions of the MBO model.
ENGINEERING VOLATILE OIL RESERVOIRS
Volatile oil reservoirs require the same PVT properties as black oil reservoirs
(in addition to the vaporized oil gas ratio) for engineering calculations. In
general, liquid recovery from surface separators in volatile oil is more sensi-
tive to separator conditions than in black oils. Figs. 6.5 6.8 show the effect
of separator conditions on MBO PVT properties for a typical volatile oil.
These properties were calculated at two different separator conditions using
an EOS and Whitson and Torp (1983) procedure. In this example, all MBO
PVT properties are affected by separator conditions except gas formation
volume factor.
Problem 1—Calculation of Volatile Oil PVT Properties for
Different Two-Stage Separator Conditions
The following represents the results of three two-stage separator experiments
for a volatile oil. Use the total solution GOR (with other field measured