Page 144 - PVT Property Correlations
P. 144
Volatile Oils Chapter | 6 121
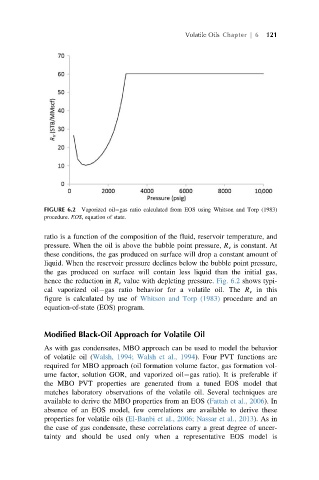
FIGURE 6.2 Vaporized oil gas ratio calculated from EOS using Whitson and Torp (1983)
procedure. EOS, equation of state.
ratio is a function of the composition of the fluid, reservoir temperature, and
pressure. When the oil is above the bubble point pressure, R v is constant. At
these conditions, the gas produced on surface will drop a constant amount of
liquid. When the reservoir pressure declines below the bubble point pressure,
the gas produced on surface will contain less liquid than the initial gas,
hence the reduction in R v value with depleting pressure. Fig. 6.2 shows typi-
cal vaporized oil gas ratio behavior for a volatile oil. The R v in this
figure is calculated by use of Whitson and Torp (1983) procedure and an
equation-of-state (EOS) program.
Modified Black-Oil Approach for Volatile Oil
As with gas condensates, MBO approach can be used to model the behavior
of volatile oil (Walsh, 1994; Walsh et al., 1994). Four PVT functions are
required for MBO approach (oil formation volume factor, gas formation vol-
ume factor, solution GOR, and vaporized oil gas ratio). It is preferable if
the MBO PVT properties are generated from a tuned EOS model that
matches laboratory observations of the volatile oil. Several techniques are
available to derive the MBO properties from an EOS (Fattah et al., 2006). In
absence of an EOS model, few correlations are available to derive these
properties for volatile oils (El-Banbi et al., 2006; Nassar et al., 2013). As in
the case of gas condensate, these correlations carry a great degree of uncer-
tainty and should be used only when a representative EOS model is