Page 86 - Partition & Adsorption of Organic Contaminants in Environmental Systems
P. 86
CORRELATIONS OF PARTITION COEFFICIENTS 77
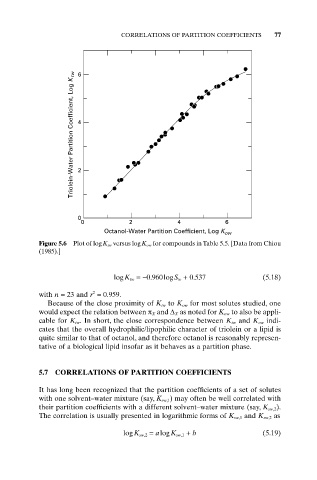
Triolein-Water Partition Coefficient, Log K tw
6
4
2
0
0 2 4 6
Octanol-Water Partition Coefficient, Log K
ow
Figure 5.6 Plot of logK tw versus logK ow for compounds in Table 5.5. [Data from Chiou
(1985).]
logK tw =-0.960logS w + 0.537 (5.18)
2
with n = 23 and r = 0.959.
Because of the close proximity of K tw to K ow for most solutes studied, one
would expect the relation between p X and D X as noted for K ow to also be appli-
cable for K tw . In short, the close correspondence between K tw and K ow indi-
cates that the overall hydrophilic/lipophilic character of triolein or a lipid is
quite similar to that of octanol, and therefore octanol is reasonably represen-
tative of a biological lipid insofar as it behaves as a partition phase.
5.7 CORRELATIONS OF PARTITION COEFFICIENTS
It has long been recognized that the partition coefficients of a set of solutes
with one solvent–water mixture (say, K sw,1 ) may often be well correlated with
their partition coefficients with a different solvent–water mixture (say, K sw,2 ).
The correlation is usually presented in logarithmic forms of K sw,1 and K sw,2 as
logK sw,2 = alogK sw,1 + b (5.19)