Page 91 - Partition & Adsorption of Organic Contaminants in Environmental Systems
P. 91
82 CONTAMINANT PARTITION AND BIOCONCENTRATION
6
Rainbow trout
Bioconcentration Factor, Log (BCF) lipid 4
Guppies
2
0
0 2 4 6
Triolein-Water Partition Coefficient, Log K
tw
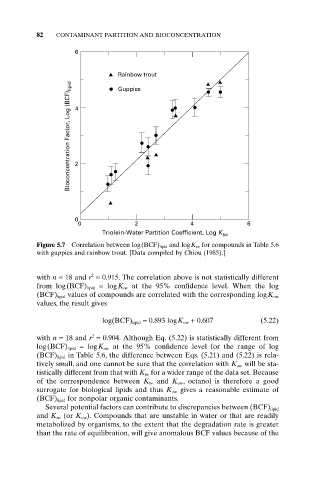
Figure 5.7 Correlation between log(BCF) lipid and logK tw for compounds in Table 5.6
with guppies and rainbow trout. [Data compiled by Chiou (1985).]
2
with n = 18 and r = 0.915. The correlation above is not statistically different
from log(BCF) lipid = logK tw at the 95% confidence level. When the log
(BCF) lipid values of compounds are correlated with the corresponding logK ow
values, the result gives
log(BCF) lipid = 0.893 logK ow + 0.607 (5.22)
2
with n = 18 and r = 0.904. Although Eq. (5.22) is statistically different from
log(BCF) lipid = logK ow at the 95% confidence level for the range of log
(BCF) lipid in Table 5.6, the difference between Eqs. (5.21) and (5.22) is rela-
tively small, and one cannot be sure that the correlation with K ow will be sta-
tistically different from that with K tw for a wider range of the data set. Because
of the correspondence between K tw and K ow , octanol is therefore a good
surrogate for biological lipids and thus K ow gives a reasonable estimate of
(BCF) lipid for nonpolar organic contaminants.
Several potential factors can contribute to discrepancies between (BCF) lipid
and K tw (or K ow ). Compounds that are unstable in water or that are readily
metabolized by organisms, to the extent that the degradation rate is greater
than the rate of equilibration, will give anomalous BCF values because of the