Page 90 - Partition & Adsorption of Organic Contaminants in Environmental Systems
P. 90
BIOCONCENTRATION OF ORGANIC CONTAMINANTS 81
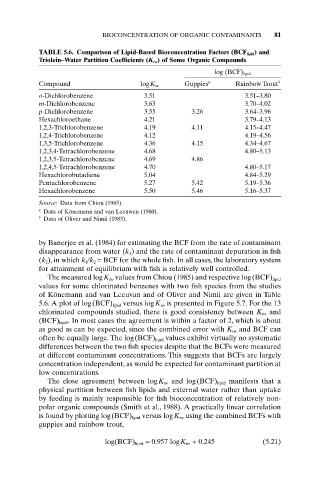
TABLE 5.6. Comparison of Lipid-Based Bioconcentration Factors (BCF lipid) and
Triolein–Water Partition Coefficients (K tw) of Some Organic Compounds
log (BCF) lipid
Compound logK tw Guppies a Rainbow Trout b
o-Dichlorobenzene 3.51 3.51–3.80
m-Dichlorobenzene 3.63 3.70–4.02
p-Dichlorobenzene 3.55 3.26 3.64–3.96
Hexachloroethane 4.21 3.79–4.13
1,2,3-Trichlorobenzene 4.19 4.11 4.15–4.47
1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene 4.12 4.19–4.56
1,3,5-Trichlorobenzene 4.36 4.15 4.34–4.67
1,2,3,4-Tetrachlorobenzene 4.68 4.80–5.13
1,2,3,5-Tetrachlorobenzene 4.69 4.86
1,2,4,5-Tetrachlorobenzene 4.70 4.80–5.17
Hexachlorobutadiene 5.04 4.84–5.29
Pentachlorobenzene 5.27 5.42 5.19–5.36
Hexachlorobenzene 5.50 5.46 5.16–5.37
Source: Data from Chiou (1985).
a
Data of Könemann and van Leeuwen (1980).
b
Data of Oliver and Nimii (1983).
by Banerjee et al. (1984) for estimating the BCF from the rate of contaminant
disappearance from water (k 1) and the rate of contaminant depuration in fish
(k 2), in which k 1/k 2 = BCF for the whole fish. In all cases, the laboratory system
for attainment of equilibrium with fish is relatively well controlled.
The measured logK tw values from Chiou (1985) and respective log(BCF) lipid
values for some chlorinated benzenes with two fish species from the studies
of Könemann and van Leeuvan and of Oliver and Nimii are given in Table
5.6. A plot of log(BCF) lipid versus logK tw is presented in Figure 5.7. For the 13
chlorinated compounds studied, there is good consistency between K tw and
(BCF) lipid . In most cases the agreement is within a factor of 2, which is about
as good as can be expected, since the combined error with K tw and BCF can
often be equally large. The log(BCF) lipid values exhibit virtually no systematic
differences between the two fish species despite that the BCFs were measured
at different contaminant concentrations. This suggests that BCFs are largely
concentration independent, as would be expected for contaminant partition at
low concentrations.
The close agreement between logK tw and log(BCF) lipid manifests that a
physical partition between fish lipids and external water rather than uptake
by feeding is mainly responsible for fish bioconcentration of relatively non-
polar organic compounds (Smith et al., 1988). A practically linear correlation
is found by plotting log(BCF) lipid versus logK tw using the combined BCFs with
guppies and rainbow trout,
log(BCF) lipid = 0.957 logK tw + 0.245 (5.21)