Page 162 - Percolation Models for Transport in Porous Media With
P. 162
9.1 SANDY-ARGILLACEOUS MEDIUM 159
10
J 2
o~--~~----~--~~
10 20 f, tnin
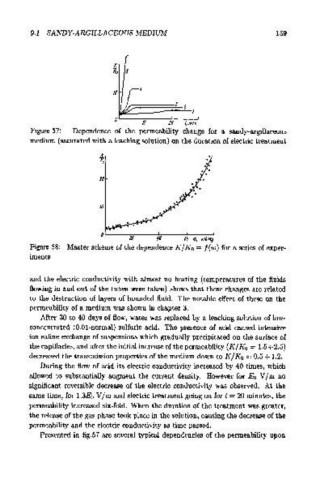
Figure 57: Dependence of the permeability change for a sandy-argillaceous
medium (saturated with a leaching solution) on the duration of electric treatment
20
10
o~----~----~----~~--~
20 to 00 "'· W./r/Jrg
Figure 58: Master scheme of the dependence I< I I< 0 = f ( w) for a series of exper-
iments
and the electric conductivity with almost no heating (temperatures of the fluids
flowing in and out of the tubes were taken) shows that these changes are related
to the destruction of layers of bounded fluid. The notable effect of these on the
permeability of a medium was shown in chapter 3.
After 30 to 40 days of flow, water was replaced by a leaching solution of low-
concentrated {0.01-normal) sulfuric acid. The presence of acid caused intensive
ion-saline exchange of suspensions which gradually precipitated on the surface of
the capillaries, and after the initial increase of the permeability {I< I I<0 = 1.5+ 2.5)
decreased the transmission properties of the medium down to I< I I<0 = 0.5 + 1.2.
During the flow of acid its electric conductivity increased by 40 times, which
allowed to substantially augment the current density. However for Eo V lm no
significant reversible decrease of the electric conductivity was observed. At the
same time, for 1.3E 0 V lm and electric treatment going on fort= 20 minutes, the
permeability increased six-fold. When the duration of the treatment was greater,
the release of the gas phase took place in the solution, causing the decrease of the
permeability and the electric conductivity as time passed.
Presented in fig.57 are several typical dependencies of the permeability upon