Page 30 - Percolation Models for Transport in Porous Media With
P. 30
1.3 EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT 21
K l'
K,z,
I
1.'":---~-L--,...J
D,.f 7 t/f,
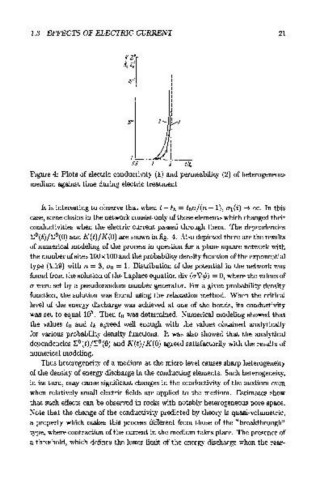
Figure 4: Plots of electric conductivity (1) and permeability (2) of heterogeneous
medium against time during electric treatment
It is interesting to observe that when t- tk = ton/(n- 1), u1 (t) ~ oo. In this
case, some chains in the network consist only of those elements which changed their
conductivities when the electric current passed through them. The dependencies
E 0 (t)/E 0 (0) and K(t)/ K(O) are shown in fig. 4. Also depicted there are the results
of numerical modeling of the process in question for a plane square network with
the number of sites 100 x 100 and the probability density function of the exponential
type (1.19) with n = 3, uo = 1. Distribution of the potential in the network was
found from the solution of the Laplace equation div (a\1¢) = 0, where the values of
a were set by a pseudorandom number generator. For a given probability density
function, the solution was found using the relaxation method. When the critical
level of the energy discharge was achieved at one of the bonds, its conductivity
5
was set to equal 10 . Then to was determined. Numerical modeling showed that
the values t 0 and tk agreed well enough with the values obtained analytically
for various probability density functions. It was also showed that the analytical
dependencies E 0 (t)/E 0 (0) and K(t)f K(O) agreed satisfactorily with the results of
numerical modeling.
Thus heterogeneity of a medium at the micro level causes sharp heterogeneity
of the density of energy discharge in the conducting elements. Such heterogeneity,
in its turn, may cause significant changes in the conductivity of the medium even
when relatively small electric fields are applied to the medium. Estimates show
that such effects can be observed in rocks with notably heterogeneous pore space.
Note that the change of the conductivity predicted by theory is quasi-volumetric,
a property which makes this process different from those of the "breakthrough"
type, where contraction of the current in the medium takes place. The presence of
a threshold, which defines the lower limit of the energy discharge when the rear-