Page 161 - Performance Leadership
P. 161
150 • Part III Principles from the Values and Social Dimensions
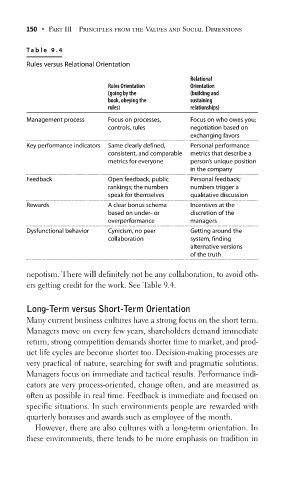
Table 9.4
Rules versus Relational Orientation
Relational
Rules Orientation Orientation
(going by the (building and
book, obeying the sustaining
rules) relationships)
Management process Focus on processes, Focus on who owes you;
controls, rules negotiation based on
exchanging favors
Key performance indicators Same clearly defined, Personal performance
consistent, and comparable metrics that describe a
metrics for everyone person’s unique position
in the company
Feedback Open feedback, public Personal feedback;
rankings; the numbers numbers trigger a
speak for themselves qualitative discussion
Rewards A clear bonus schema Incentives at the
based on under- or discretion of the
overperformance managers
Dysfunctional behavior Cynicism, no peer Getting around the
collaboration system, finding
alternative versions
of the truth
nepotism. There will definitely not be any collaboration, to avoid oth-
ers getting credit for the work. See Table 9.4.
Long-Term versus Short-Term Orientation
Many current business cultures have a strong focus on the short term.
Managers move on every few years, shareholders demand immediate
return, strong competition demands shorter time to market, and prod-
uct life cycles are become shorter too. Decision-making processes are
very practical of nature, searching for swift and pragmatic solutions.
Managers focus on immediate and tactical results. Performance indi-
cators are very process-oriented, change often, and are measured as
often as possible in real time. Feedback is immediate and focused on
specific situations. In such environments people are rewarded with
quarterly bonuses and awards such as employee of the month.
However, there are also cultures with a long-term orientation. In
these environments, there tends to be more emphasis on tradition in