Page 184 - Petroleum Geology
P. 184
161
authigenic minerals, particularly clays, may form in the pore spaces (see Plate
8-1). These have the effect of reducing porosity and increasing the specific
surface, and both tend to reduce the permeability of the rock. Even if the
specific surface is increased by two orders of magnitude, most of the water
saturation will still be due to free water trapped at grain contacts and in small
pores.
Pressures
Within the oil reservoir, above the level at which the oil forms a continuous
phase (which we take to be the oil/water contact), the pressure in the oil
decreases upwards according to the relationship:
where po is the mean mass density of the oil. This pressure is imposed on the
pendular rings of water, which, because they are isolated from each other,
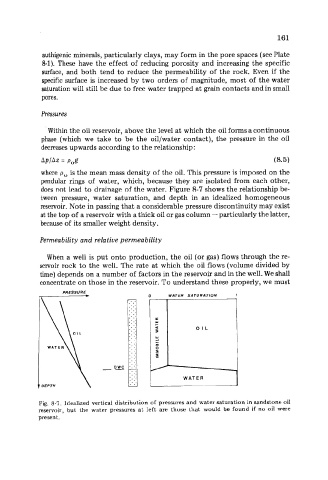
does not lead to drainage of the water. Figure 8-7 shows the relationship be-
tween pressure, water saturation, and depth in an idealized homogeneous
reservoir. Note in passing that a considerable pressure discontinuity may exist
at the top of a reservoir with a thick oil or gas column - particularly the latter,
because of its smaller weight density.
Permeability and relative permeability
When a well is put onto production, the oil (or gas) flows through the re-
servoir rock to the well. The rate at which the oil flows (volume divided by
time) depends on a number of factors in the reservoir and in the well. We shall
concentrate on those in the reservoir. To understand these properly, we must
PRESSURE
..
.. 1 ..
..
..
..
..
..
--
OWC 5
..
..
..
..
..
Fig. 8-7. Idealized vertical distribution of pressures and water saturation in sandstone oil
reservoir, but the water pressures at left are those that would be found if no oil were
present.