Page 113 - Petroleum and Gas Field Processing
P. 113
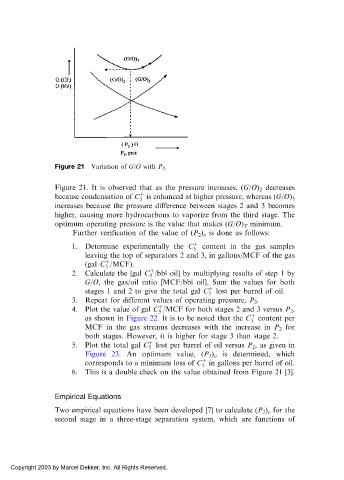
Figure 21 Variation of G/O with P 2 .
Figure 21. It is observed that as the pressure increases, (G/O) 2 decreases
þ
5
because condensation of C is enhanced at higher pressure, whereas (G/O) 3
increases because the pressure difference between stages 2 and 3 becomes
higher, causing more hydrocarbons to vaporize from the third stage. The
optimum operating pressure is the value that makes (G/O) T minimum.
Further verification of the value of (P 2 ) o is done as follows:
1. Determine experimentally the C þ content in the gas samples
5
leaving the top of separators 2 and 3, in gallons/MCF of the gas
þ
(gal C /MCF).
5
þ
2. Calculate the [gal C /bbl oil] by multiplying results of step 1 by
5
G/O, the gas/oil ratio [MCF/bbl oil]. Sum the values for both
stages 1 and 2 to give the total gal C þ lost per barrel of oil.
5
3. Repeat for different values of operating pressure, P 2 .
þ
4. Plot the value of gal C /MCF for both stages 2 and 3 versus P 2 ,
5
þ
as shown in Figure 22. It is to be noted that the C content per
5
MCF in the gas streams decreases with the increase in P 2 for
both stages. However, it is higher for stage 3 than stage 2.
þ
5. Plot the total gal C lost per barrel of oil versus P 2 , as given in
5
Figure 23. An optimum value, (P 2 ) o is determined, which
þ
corresponds to a minimum loss of C in gallons per barrel of oil.
5
6. This is a double check on the value obtained from Figure 21 [3].
Empirical Equations
Two empirical equations have been developed [7] to calculate (P 2 ) o for the
second stage in a three-stage separation system, which are functions of
Copyright 2003 by Marcel Dekker, Inc. All Rights Reserved.