Page 320 - Petroleum and Gas Field Processing
P. 320
Thus the diameter is
r ffiffiffiffiffiffi
4A
D ¼ ð7Þ
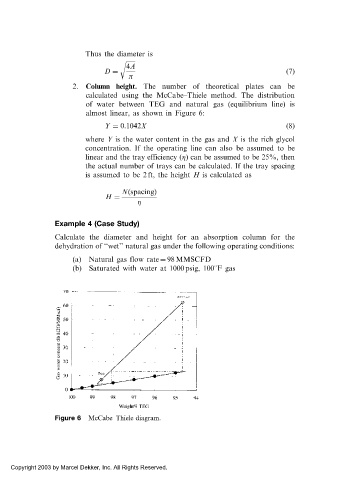
2. Column height. The number of theoretical plates can be
calculated using the McCabe–Thiele method. The distribution
of water between TEG and natural gas (equilibrium line) is
almost linear, as shown in Figure 6:
Y ¼ 0:1042X ð8Þ
where Y is the water content in the gas and X is the rich glycol
concentration. If the operating line can also be assumed to be
linear and the tray efficiency ( ) can be assumed to be 25%, then
the actual number of trays can be calculated. If the tray spacing
is assumed to be 2 ft, the height H is calculated as
NðspacingÞ
H ¼
Example 4 (Case Study)
Calculate the diameter and height for an absorption column for the
dehydration of ‘‘wet’’ natural gas under the following operating conditions:
(a) Natural gas flow rate ¼ 98 MMSCFD
(b) Saturated with water at 1000 psig, 100 F gas
Figure 6 McCabe–Thiele diagram.
Copyright 2003 by Marcel Dekker, Inc. All Rights Reserved.