Page 104 - Petrophysics 2E
P. 104
PETROLEUM CHEMISTRY 77
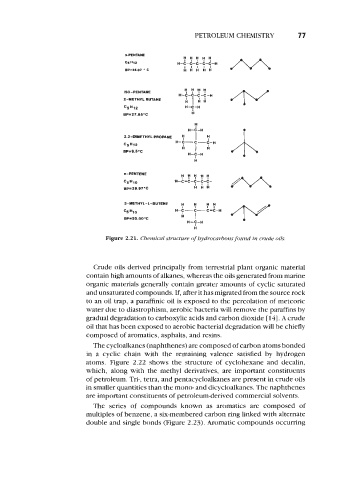
n-PENTANE rrrr?
C5H12 H-C-C-C-C-C-H I
I
I
I
BP=36.07 ' C A H H H H
HHH$I
150-PENTANE H-C-C-C -C -H
2-METHYL BUTANE A I AA
'gH12 H-C-H
BP=27.85°C A
H
7 I ?
H-C-H
2.2-DIMETHYLPROPANE H
H-c-c-J-H
C5H12 e l l s
BP=9.SDC
H-C-H
H
c c 77
3-METHYL-L-BUTENE
H-C-C-CCIC-H
'5 H1O
BP=20.OOoC A I
H-C-H
H
Figure 2.21. Chemical structure of hydrocarbons found in crude oils.
Crude oils derived principally from terrestrial plant organic material
contain high amounts of alkanes, whereas the oils generated from marine
organic materials generally contain greater amounts of cyclic saturated
and unsaturated compounds. If, after it has migrated from the source rock
to an oil trap, a paraffinic oil is exposed to the percolation of meteoric
water due to diastrophism, aerobic bacteria will remove the paraffins by
gradual degradation to carboxylic acids and carbon dioxide [ 141. A crude
oil that has been exposed to aerobic bacterial degradation will be chiefly
composed of aromatics, asphalts, and resins.
The cycloalkanes (naphthenes) are composed of carbon atoms bonded
in a cyclic chain with the remaining valence satisfied by hydrogen
atoms. Figure 2.22 shows the structure of cyclohexane and decalin,
which, along with the methyl derivatives, are important constituents
of petroleum. Tri-, tetra, and pentacycloalkanes are present in crude oils
in smaller quantities than the mono- and dicycloalkanes. The naphthenes
are important constituents of petroleum-derived commercial solvents.
The series of compounds known as aromatics are composed of
multiples of benzene, a six-membered carbon ring linked with alternate
double and single bonds (Figure 2.23). Aromatic compounds occurring