Page 293 - Phase Space Optics Fundamentals and Applications
P. 293
274 Chapter Eight
νx
p/n 0
7
6 0.4
5 0.3
4 0.2
νx s 0.1
2 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
νx 0 –0.1 νx
–0.2
2 4 6 8 10
νz
(a) (b)
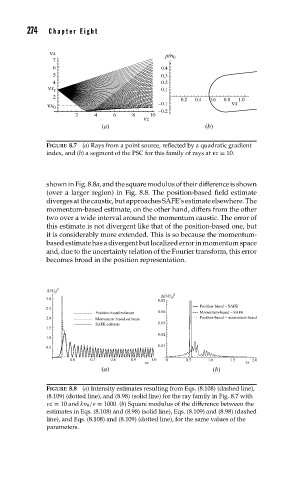
FIGURE 8.7 (a) Rays from a point source, reflected by a quadratic gradient
index, and (b) a segment of the PSC for this family of rays at z = 10.
shown in Fig. 8.8a, and the square modulus of their difference is shown
(over a larger region) in Fig. 8.8. The position-based field estimate
divergesatthecaustic,butapproachesSAFE’sestimateelsewhere.The
momentum-based estimate, on the other hand, differs from the other
two over a wide interval around the momentum caustic. The error of
this estimate is not divergent like that of the position-based one, but
it is considerably more extended. This is so because the momentum-
based estimate has a divergent but localized error in momentum space
and, due to the uncertainty relation of the Fourier transform, this error
becomes broad in the position representation.
2
|U/U 0 |
2
|ΔU/U 0 |
3.0 0.05
Position-based – SAFE
2.5
Position-based estimate 0.04 Momentum-based – SAFE
2.0 Momentum-based estimate Position-based – momentum-based
SAFE estimate 0.03
1.5
0.02
1.0
0.01
0.5
0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0 0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0
νx νx
(a) (b)
FIGURE 8.8 (a) Intensity estimates resulting from Eqs. (8.108) (dashed line),
(8.109) (dotted line), and (8.98) (solid line) for the ray family in Fig. 8.7 with
z = 10 and kn 0 / = 1000. (b) Square modulus of the difference between the
estimates in Eqs. (8.108) and (8.98) (solid line), Eqs. (8.109) and (8.98) (dashed
line), and Eqs. (8.108) and (8.109) (dotted line), for the same values of the
parameters.